Preliminary
18 Mb Burst of 2 Pipelined SRAM with QDR Architecture
CY7C1303V25
CY7C1306V25
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation
∑
3901 North First Street
∑
San Jose
∑
CA 95134
∑
408-943-2600
Document #: 38-05100 Rev. *A
Revised December 11, 2002
yy yy yy
Features
∑ Separate Independent Read and Write Data Ports
-- Supports concurrent transactions
∑ 167 MHz Clock for High Bandwidth
-- 2.5 ns Clock-to-Valid access time
∑ 2-Word Burst on all accesses
∑ Double Data Rate (DDR) interfaces on both Read & Write
Ports (data transferred at 333 MHz) @167 MHz
∑ Two input clocks (K and K) for precise DDR timing
-- SRAM uses rising edges only
∑ Two output clocks (C and C) accounts for clock skew
and flight time mis-matches
∑ Single multiplexed address input bus latches address
inputs for both READ and WRITE ports
∑ Separate Port Selects for depth expansion
∑ Synchronous internally self-timed writes
∑ 2.5V core power supply with HSTL Inputs and Outputs
∑ 13x15 mm 1.0 mm pitch fBGA package, 165 ball
(11x15 matrix) Variable drive HSTL output buffers
∑ Expanded HSTL output voltage (1.4V≠1.9V)
∑ JTAG Interface
∑ Variable Impedance HSTL
Configurations
CY7C1303V25 ≠ 1 Mb x 18
CY7C1306V25 ≠ 512K x 36
Functional Description
The CY7C1303V25 and CY7C1306V25 are 2.5V Synchro-
nous Pipelined SRAMs equipped with QDR architecture. QDR
architecture consists of two separate ports to access the mem-
ory array. The Read port has dedicated Data Outputs to sup-
port Read operations and the Write Port has dedicated Data
inputs to support Write operations. Access to each port is ac-
complished through a common address bus. The Read ad-
dress is latched on the rising edge of the K clock and the Write
address is latched on the rising edge of K clock. QDR has
separate data inputs and data outputs to completely eliminate
the need to "turn-around" the data bus required with common
I/O devices. Accesses to the CY7C1303V25/CY7C1306V25
Read and Write ports are completely independent of one an-
other. All accesses are initiated synchronously on the rising
edge of the positive input clock (K). In order to maximize data
throughput, both Read and Write ports are equipped with Dou-
ble Data Rate (DDR) interfaces. Therefore, data can be trans-
ferred into the device on every rising edge of both input clocks
(K and K) and out of the device on every rising edge of the
output clock (C and C) thereby maximizing performance while
simplifying system design. Each address location is associat-
ed with two 18-bit words (CY7C1303V25) or two 36-bit words
(CY7C1306V25) that burst sequentially into or out of the de-
vice.
Depth expansion is accomplished with a Port Select input for
each port. Each Port Selects allow each port to operate inde-
pendently.
All synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled
by the K or K input clocks. All data outputs pass through output
registers controlled by the C or C input clocks. Writes are con-
ducted with on-chip synchronous self-timed write circuitry.
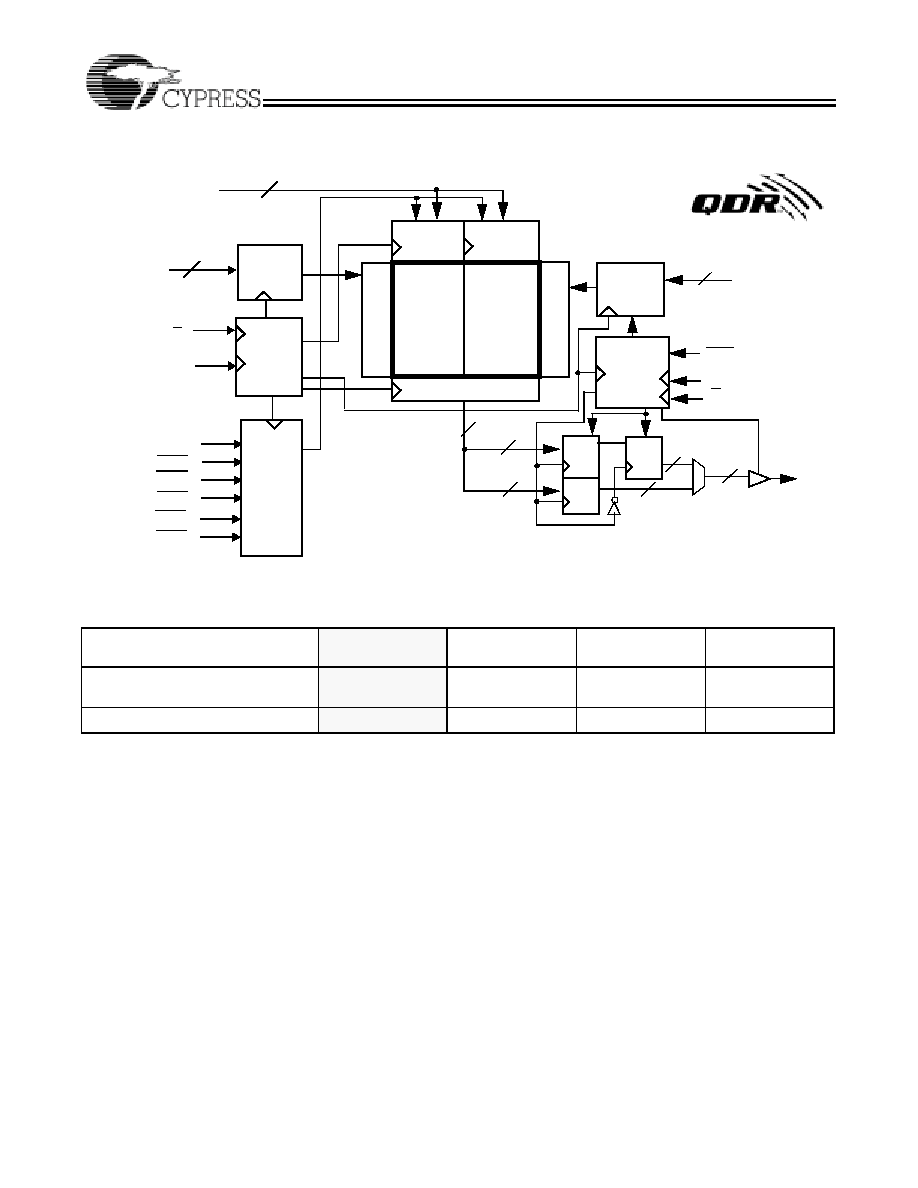
Logic Block Diagram (CY7C1303V25)
512Kx18
CLK
A
(18:0)
Gen.
K
K
Control
Logic
Address
Register
D
[17:0]
Read
Ad
d
.
Deco
d
e
Read Data Reg.
RPS
WPS
Q
[17:0]
Control
Logic
Address
Register
Reg.
Reg.
Reg.
18
19
18
36
Write
18
BWS
0
Vref
W
r
i
t
e Ad
d
.
Deco
d
e
Data Reg
Write
Data Reg
Memory
Array
512Kx18
Memory
Array
18
18
A
(18:0)
19
18
C
C
BWS
1
CY7C1303V25
CY7C1306V25
Preliminary
Document #: 38-05100 Rev. *A
Page 2 of 28
Selection Guide
[1]
7C1303V25-200
7C1306V25-200
7C1303V25-167
7C1306V25-167
7C1303V25-133
7C1306V25-133
7C1303V25-100
7C1306V25-100
Maximum Operating Frequency
(MHz)
200
167
133
100
Maximum Operating Current (mA)
TBD
550
450
330
Note:
1.
Sheaded cells indicate advanced information.
Logic Block Diagram (CY7C1306V25)
256Kx36
CLK
A
(17:0)
Gen.
K
K
Control
Logic
Address
Register
D
[35:0]
R
ead
Ad
d
.
D
eco
d
e
Read Data Reg.
RPS
WPS
Q
[35:0]
Control
Logic
Address
Register
Reg.
Reg.
Reg.
36
18
36
72
Write
36
BWS
0
Vref
W
r
i
t
e Ad
d
.
D
eco
d
e
Data Reg
Write
Data Reg
Memory
Array
256Kx36
Memory
Array
36
36
A
(17:0)
18
36
C
C
BWS
1
BWS
2
BWS
3
CY7C1303V25
CY7C1306V25
Preliminary
Document #: 38-05100 Rev. *A
Page 5 of 28
Pin Definitions
Name
I/O
Description
D
[x:0]
Input-
Synchronous
Data input signals, sampled on the rising edge of K and K clocks during valid write
operations.
CY7C1303V25 ≠ D
[17:0]
CY7C1306V25 ≠ D
[35:0]
WPS
Input-
Synchronous
Write Port Select, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of the K clock. When asserted
active, a write operation is initiated. Deasserting will deselect the Write port. Deselecting
the Write port will cause D
[x:0]
to be ignored.
BWS
0
, BWS
1
,
BWS
2
, BWS
3
Input-
Synchronous
Byte Write Select 0, 1, 2 and 3 - active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of the K and
K clocks during write operations. Used to select which byte is written into the device
during the current portion of the write operations.
CY7C1303V25 - BWS
0
controls D
[8:0]
and BWS
1
controls D
[17:9].
CY7C1306V25 - BWS
0
controls D
[8:0]
, BWS
1
controls D
[17:9]
, BWS
2
controls D
[26:18]
and BWS
3
controls D
[35:27]
Bytes not written remain unaltered. Deselecting a Byte Write Select will cause the cor-
responding byte of data to be ignored and not written into the device.
A
Input-
Synchronous
Address Inputs. Sampled on the rising edge of the K clock during active Read operations
and on the rising edge of K for Write operations. These address inputs are multiplexed
for both Read and Write operations. Internally, the device is organized as 1 Mb x 18 (2
arrays each of 512K x 18) for CY7C1303V25 and 512K x 36 (2 arrays each of 256K x
36) for CY7C1306V25. Therefore, only 19 address inputs are needed to access the
entire memory array of CY7C1303V25 and 18 address inputs for CY7C1306V25. These
inputs are ignored when the appropriate port is deselected.
Q
[x:0]
Outputs-
Synchronous
Data Output signals. These pins drive out the requested data during a Read operation.
Valid data is driven out on the rising edge of both the C and C clocks during Read
operations or K and K. when in single clock mode. When the Read port is deselected,
Q
[x:0]
are automatically three-stated.
CY7C1303V25 - Q
[17:0]
CY7C1306V25 - Q
[35:0]
RPS
Input-
Synchronous
Read Port Select, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of positive input clock (K).
When active, a Read operation is initiated. Deasserting will cause the Read port to be
deselected. When deselected, the pending access is allowed to complete and the output
drivers are automatically three-stated following the next rising edge of the K clock. Each
read access consists of a burst of two sequential 18-bit or 36-bit transfers.
C
Input-Clock
Positive Output Clock, input. C is used in conjunction with C to clock out the Read data
from the device. C and C can be used together to deskew the flight times of various
devices on the board back to the controller. See application example for further details.
C
Input-Clock
Negative Output Clock, input. C is used in conjunction with C to clock out the Read data
from the device. C and C can be used together to deskew the flight times of various
devices on the board cack to the controller. See application example for further details.
K
Input-Clock
Positive Input Clock, input. The rising edge of K is used to capture synchronous inputs
to the device and to drive out data through Q
[x:0]
when in single clock mode. All accesses
are initiated on the rising edge of K.
K
Input-Clock
Negative Input Clock Input. K is used to capture synchronous inputs being presented
to the device and to drive out data through Q
[x:0]
when in single clock mode.
ZQ
Input
Output Impedance Matching Input. This input is used to tune the device outputs to the
system data bus impedance. Q
[x:0]
output impedance are set to 0.2 x RQ, where RQ is
a resistor connected between ZQ and ground. Alternately, this pin can be connected
directly to V
DD
, which enables the minimum impedance mode. This pin cannot be con-
nected directly to GND or left unconnected.