 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: CY7C1353B | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
PRELIMINARY
256Kx18 Flow-Through SRAM with NoBLTM Architecture
CY7C1353B
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation
∑
3901 North First Street
∑
San Jose
∑
CA 95134
∑
408-943-2600
Document #: 38-05266 Rev. **
Revised March 13, 2002
353B
Features
∑ Pin compatible and functionally equivalent to ZBTTM
devices MCM63Z819 and MT55L256L18F
∑ Supports 117-MHz bus operations with zero wait states
-- Data is transferred on every clock
∑ Internally self-timed output buffer control to eliminate
the need to use OE
∑ Registered inputs for flow-through operation
∑ Byte Write capability
∑ 256K x 18 common I/O architecture
∑ Single 3.3V power supply
∑ Fast clock-to-output times
-- 7.5 ns (for 117- MHz device)
-- 8.5 ns (for 100-MHz device)
-- 11.0 ns (for 66-MHz device)
-- 12. 0 ns (for 50-MHz device)
-- 14.0 ns (for 40-MHz device)
∑ Clock Enable (CEN) pin to suspend operation
∑ Synchronous self-timed writes
∑ Asynchronous Output Enable
∑ JEDEC-standard 100 TQFP package
∑ Burst Capability--linear or interleaved burst order
∑ Low standby power
Functional Description
The CY7C1353B is a 3.3V, 256K by 18 Synchronous
Flow-Through Burst SRAM designed specifically to support
unlimited true back-to-back Read/Write operations without the
insertion of wait states. The CY7C1353B is equipped with the
advanced No Bus LatencyTM (NoBLTM) logic required to en-
able consecutive Read/Write operations with data being trans-
ferred on every clock cycle. This feature dramatically improves
the throughput of data through the SRAM, especially in sys-
tems that require frequent Write-Read transitions. The
CY7C1353B is pin/functionally compatible to ZBT SRAMs
MCM63Z819 and MT55L256L18F.
All synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled
by the rising edge of the clock. The clock input is qualified by
the Clock Enable (CEN) signal, which when deasserted sus-
pends operation and extends the previous clock cycle. Maxi-
mum access delay from the clock rise is 7.5 ns (117-MHz de-
vice).
Write operations are controlled by the four Byte Write Select
(BWS
[1:0]
) and a Write Enable (WE) input. All writes are con-
ducted with on-chip synchronous self-timed write circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Enables (CE
1
, CE
2
, CE
3
) and an
asynchronous Output Enable (OE) provide for easy bank se-
lection and output three-state control. In order to avoid bus
contention, the output drivers are synchronously three-stated
during the data portion of a write sequence.
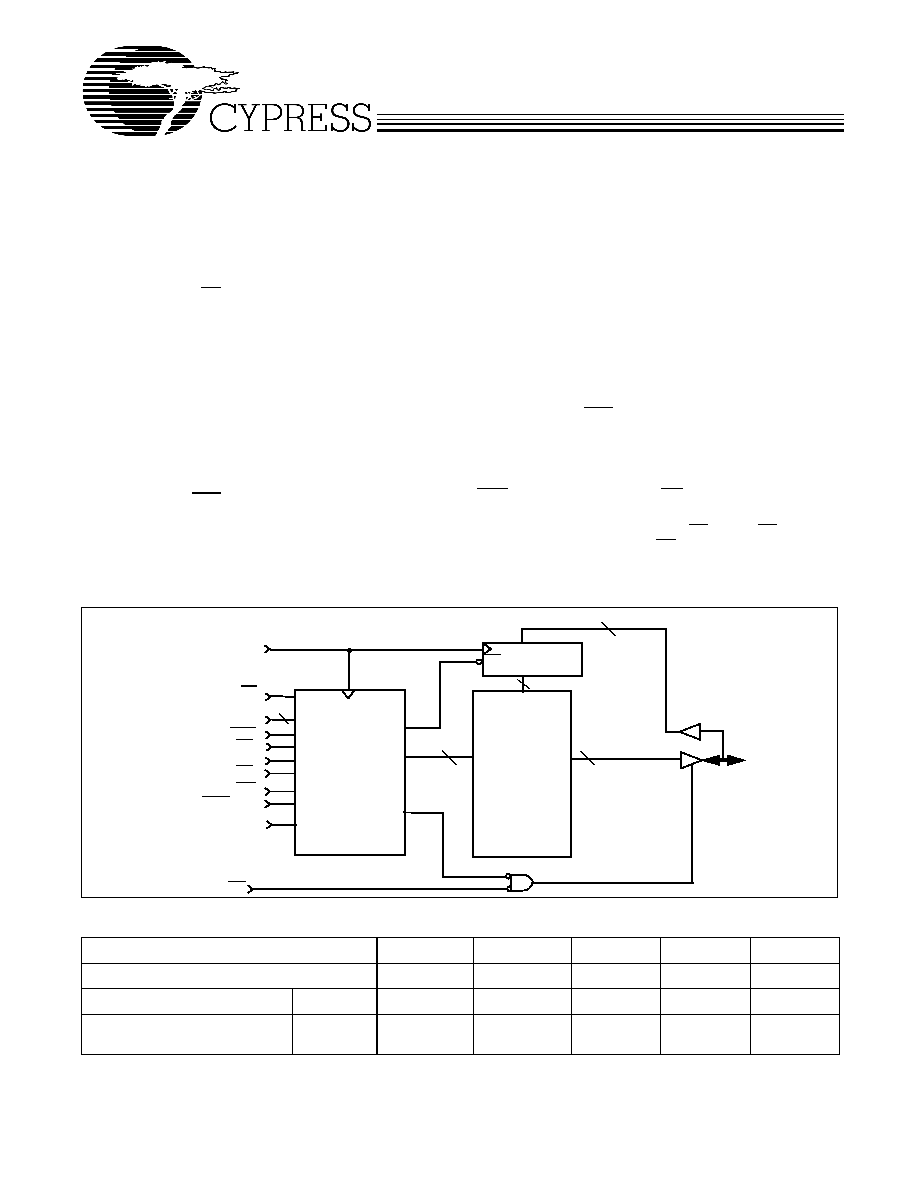
CLK
A
[17:0]
CEN
WE
BWS
CE1
CE
CE 2
OE
256KX18
MEMORY
ARRAY
Logic Block Diagram
DQ
[15:0]
Data-In REG.
Q
D
CE
CONTROL
and WRITE
LOGIC
3
[1:0]
ADV/LD
18
18
18
18
18
Mode
DP
[1:0]
Selection Guide
7C1353B-117
7C1353B-100
7C1353B-66
7C1353B-50
7C1353B-40
Maximum Access Time (ns)
7.5
8.5
11.0
12.0
14.0
Maximum Operating Current (mA) Commercial
375
350
250
200
175
Maximum CMOS Standby
Current (mA)
Commercial
5
5
5
5
5
NoBL and No Bus Latency are trademarks of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation.
ZBT is a trademark of Integrated Device Technology.

CY7C1353B
PRELIMINARY
Document #: 38-05266 Rev. **
Page 2 of 15
Pin Configurations
100-Pin TQFP
A
5
A
4
A
3
A
2
A
1
A
0
DNU
DNU
V
SS
V
DD
DN
U
A
10
A
11
A
12
A
13
A
14
A
16
A
17
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
NC
DP
0
DQ
7
DQ
6
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
5
DQ
4
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
DQ
3
DQ
2
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
1
DQ
0
NC
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
NC
NC
DQ
8
DQ
9
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
10
DQ
11
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
DQ
12
DQ
13
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
14
DQ
15
DP
1
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
A6
A7
CE
1
CE
2
NC
NC
BWS
1
BWS
0
CE
3
V
DD
V
SS
CLK
WE
CE
N
OE
NC
A
8
A
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
10
0
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
A
15
NC
AD
V
/
LD
V
SS
MO
DE
DNU
CY7C1353B

CY7C1353B
PRELIMINARY
Document #: 38-05266 Rev. **
Page 3 of 15
Û
Introduction
Pin Configurations
(continued)
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
DDQ
NC
NC
DQP
c
DQ
c
DQ
d
DQ
c
DQ
d
A
A
A
A
ADSP
V
DDQ
CE
2
A
DQ
c
V
DDQ
DQ
c
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
DQ
d
DQ
d
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
DD
CLK
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
NC
NC
V
DD
TDO
TCK
TDI
TMS
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
A
A
A
A
CE
3
A
A
A
A
A
A
A0
A1
DQ
a
DQ
c
DQ
a
DQ
a
DQ
a
DQ
b
DQ
b
DQ
b
DQ
b
DQ
b
DQ
b
DQ
b
DQ
a
DQ
a
DQ
a
DQ
a
DQ
b
V
DD
DQ
c
DQ
c
DQ
c
V
DD
DQ
d
DQ
d
DQ
d
DQ
d
ADSC
NC
CE
1
OE
ADV
GW
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
DQP
a
MODE
DQP
d
DQP
b
BW
b
BW
c
NC
V
DD
NC
BW
a
NC
BWE
BW
d
ZZ
119-Ball BGA
A
Pin Definitions
Pin Number
Name
I/O
Description
80, 50
-
44,
81
-
82, 99≠
100, 32
-
37
A
[17:0]
Input-
Synchronous
Address Inputs used to select one of the 262,144 address locations. Sampled at
the rising edge of the CLK.
94, 93
BWS
[1:0]
Input-
Synchronous
Byte Write Select Inputs, active LOW. Qualified with WE to conduct writes to the
SRAM. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. BWS
0
controls DQ
[7:0]
and DP
0
, BWS
1
controls DQ
[15:8]
and DP
1
. See Write Cycle Description table for details.
88
WE
Input-
Synchronous
Write Enable Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK if CEN is active
LOW. This signal must be asserted LOW to initiate a write sequence.
85
ADV/LD
Input-
Synchronous
Advance/Load Input used to advance the on-chip address counter or load a new
address. When HIGH (and CEN is asserted LOW) the internal burst counter is
advanced. When LOW, a new address can be loaded into the device for an access.
After being deselected, ADV/LD should be driven LOW in order to load a new
address.
89
CLK
Input-Clock
Clock Input. Used to capture all synchronous inputs to the device. CLK is qualified
with CEN. CLK is only recognized if CEN is active LOW.
98
CE
1
Input-
Synchronous
Chip Enable 1 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE
2
, and CE
3
to select/deselect the device.
97
CE
2
Input-
Synchronous
Chip Enable 2 Input, active HIGH. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE
1
and CE
3
to select/deselect the device.
92
CE
3
Input-
Synchronous
Chip Enable 3 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE and
CE
2
to select/deselect the device.

CY7C1353B
PRELIMINARY
Document #: 38-05266 Rev. **
Page 4 of 15
Functional Overview
The CY7C1353B is a synchronous flow-through burst SRAM
designed specifically to eliminate wait states during
Write-Read transitions. All synchronous inputs pass through
input registers controlled by the rising edge of the clock. The
clock signal is qualified with the Clock Enable input signal
(CEN). If CEN is HIGH, the clock signal is not recognized and
all internal states are maintained. All synchronous operations
are qualified with CEN. Maximum access delay from the clock
rise (t
CDV
) is 7.5 ns (117-MHz device).
Accesses can be initiated by asserting all three Chip Enables
(CE
1
, CE
2
, CE
3
) active at the rising edge of the clock. If Clock
Enable (CEN) is active LOW and ADV/LD is asserted LOW, the
address presented to the device will be latched. The access
can either be a read or write operation, depending on the sta-
tus of the Write Enable (WE). BWS
[1:0]
can be used to conduct
byte write operations.
Write operations are qualified by the Write Enable (WE). All
writes are simplified with on-chip synchronous self-timed write
circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Enables (CE
1
, CE
2
, CE
3
) and an
asynchronous Output Enable (OE) simplify depth expansion.
All operations (Reads, Writes, and Deselects) are pipelined.
ADV/LD should be driven LOW once the device has been de-
selected in order to load a new address for the next operation.
Single Read Accesses
A read access is initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) CEN is asserted LOW, (2) CE
1
, CE
2
,
86
OE
Input-
Asynchronous
Output Enable, active LOW. Combined with the synchronous logic block inside the
device to control the direction of the I/O pins. When LOW, the I/O pins are allowed
to behave as outputs. When deasserted HIGH, I/O pins are three-stated, and act
as input data pins. OE is masked during the data portion of a write sequence,
during the first clock when emerging from a deselected state, when the device has
been deselected.
87
CEN
Input-
Synchronous
Clock Enable Input, active LOW. When asserted LOW the Clock signal is recog-
nized by the SRAM. When deasserted HIGH the Clock signal is masked. Since
deasserting CEN does not deselect the device, CEN can be used to extend the
previous cycle when required.
23
-
22,
19
-
18,
13
-
12, 9
-
8,
73
-
72,
69
-
68,
63
-
62, 59
-
58
DQ
[15:0]
I/O-
Synchronous
Bidirectional Data I/O Lines. As inputs, they feed into an on-chip data register that
is triggered by the rising edge of CLK. As outputs, they deliver the data contained
in the memory location specified by A
[17:0]
during the previous clock rise of the
read cycle. The direction of the pins is controlled by OE and the internal control
logic. When OE is asserted LOW, the pins can behave as outputs. When HIGH,
DQ
[15:0]
are placed in a three-state condition. The outputs are automatically
three-stated during the data portion of a write sequence, during the first clock when
emerging from a deselected state, and when the device is deselected, regardless
of the state of OE.
24, 74
DP
[1:0]
I/O-
Synchronous
Bidirectional Data Parity I/O Lines. Functionally, these signals are identical to
DQ
[15:0]
. During write sequences, DP
0
is controlled by BWS
0
and DP
1
is controlled
by BWS
1
.
31
Mode
Input
Strap pin
Mode Input. Selects the burst order of the device. Tied HIGH selects the interleaved
burst order. Pulled LOW selects the linear burst order. MODE should not change
states during operation. When left floating MODE will default HIGH, to an inter-
leaved burst order.
15, 16, 41, 65,
91
V
DD
Power Supply
Power supply inputs to the core of the device. Should be connected to 3.3V power
supply.
4, 11, 20, 27,
54, 61, 70, 77
V
DDQ
I/O Power
Supply
Power supply for the I/O circuitry. Should be connected to a 3.3V power supply.
5, 10, 14, 17,
21, 26, 40, 55,
60, 64,
66
-
67, 71,
76, 90
V
SS
Ground
Ground for the device. Should be connected to ground of the system.
1
-
3, 6
-
7, 25,
28
-
30,51
-
53,
56
-
57, 75,
78
-
79, 95
-
96
NC
-
No Connects. These pins are not connected to the internal device.
83, 84
NC
-
No Connects. Reserved for address inputs for depth expansion. Pin 83 will be used
for 512K depth and pin 84 will be used for 1-Mb depth.
38, 39, 42, 43
DNU
-
Do Not Use Pins. These pins should be left floating or tied to V
SS
.
Pin Definitions
(continued)
Pin Number
Name
I/O
Description

CY7C1353B
PRELIMINARY
Document #: 38-05266 Rev. **
Page 5 of 15
and CE
3
are ALL asserted active, (3) the Write Enable input
signal WE is deasserted HIGH, and 4) ADV/LD is asserted
LOW. The address presented to the address inputs (A
[17:0]
) is
latched into the Address Register and presented to the mem-
ory core and control logic. The control logic determines that a
read access is in progress and allows the requested data to
propagate to the output buffers. The data is available within 7.5
ns (117-MHz device) provided OE is active LOW. After the first
clock of the read access the output buffers are controlled by
OE and the internal control logic. OE must be driven LOW in
order for the device to drive out the requested data. On the
subsequent clock, another operation (Read/Write/Deselect)
can be initiated. When the SRAM is deselected at clock rise
by one of the chip enable signals, its output will be three-stated
immediately.
Burst Read Accesses
The CY7C1353B has an on-chip burst counter that allows the
user the ability to supply a single address and conduct up to
four Reads without reasserting the address inputs. ADV/LD
must be driven LOW in order to load a new address into the
SRAM, as described in the Single Read Access section above.
The sequence of the burst counter is determined by the MODE
input signal. A LOW input on MODE selects a linear burst
mode, a HIGH selects an interleaved burst sequence. Both
burst counters use A0 and A1 in the burst sequence, and will
wrap around when incremented sufficiently. A HIGH input on
ADV/LD will increment the internal burst counter regardless of
the state of chip enable inputs or WE. WE is latched at the
beginning of a burst cycle. Therefore, the type of access (Read
or Write) is maintained throughout the burst sequence.
Single Write Accesses
Write access are initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) CEN is asserted LOW, (2) CE
1
, CE
2
,
and CE
3
are ALL asserted active, and (3) the write signal WE
is asserted LOW. The address presented to A
[17:0]
is loaded
into the Address Register. The write signals are latched into
the Control Logic block. The data lines are automatically
three-stated regardless of the state of the OE input signal. This
allows the external logic to present the data on DQ
[15:0]
and
DP
[1:0]
.
On the next clock rise the data presented to DQ
[15:0]
and
DP
[1:0]
(or a subset for byte write operations, see Write Cycle
Description table for details) inputs is latched into the device
and the write is complete. Additional accesses
(Read/Write/Deselect) can be initiated on this cycle.
The data written during the Write operation is controlled by
BWS
[1:0]
signals. The CY7C1353B provides byte write capa-
bility that is described in the Write Cycle Description table.
Asserting the Write Enable input (WE) with the selected Byte
Write Select (BWS
[1:0]
) input will selectively write to only the
desired bytes. Bytes not selected during a byte write operation
will remain unaltered. A synchronous self-timed write mecha-
nism has been provided to simplify the write operations. Byte
write capability has been included in order to greatly simplify
Read/Modify/Write sequences, which can be reduced to sim-
ple byte write operations.
Because the CY7C1353B is a common I/O device, data should
not be driven into the device while the outputs are active. The
Output Enable (OE) can be deasserted HIGH before present-
ing data to the DQ
[15:0]
and DP
[1:0]
inputs. Doing so will
three-state the output drivers. As a safety precaution, DQ
[15:0]
and DP
[1:0]
.are automatically three-stated during the data por-
tion of a write cycle, regardless of the state of OE.
Burst Write Accesses
The CY7C1353B has an on-chip burst counter that allows the
user the ability to supply a single address and conduct up to
four Write operations without reasserting the address inputs.
ADV/LD must be driven LOW in order to load the initial ad-
dress, as described in the Single Write Access section above.
When ADV/LD is driven HIGH on the subsequent clock rise,
the Chip Enables (CE
1
, CE
2
, and CE
3
) and WE inputs are
ignored and the burst counter is incremented. The correct
BWS
[1:0]
inputs must be driven in each cycle of the burst write
in order to write the correct bytes of data.




