 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: IRFMG50 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter
Units
ID @ VGS = 10V, TC = 25∞C
Continuous Drain Current
5.6
ID @ VGS = 10V, TC = 100∞C Continuous Drain Current
3.5
IDM
Pulsed Drain Current
22
PD @ TC = 25∞C
Max. Power Dissipation
150
W
Linear Derating Factor
1.2
W/∞C
VGS
Gate-to-Source Voltage
±20
V
EAS
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy
860
mJ
IAR
Avalanche Current
5.6
A
EAR
Repetitive Avalanche Energy
15
mJ
dv/dt
Peak Diode Recovery dv/dt
1.0
V/ns
T J
Operating Junction
-55 to 150
TSTG
Storage Temperature Range
Lead Temperature
300(0.063in./1.6mm from case for 10 sec)
Weight
9.3 (Typical)
g
PD - 90711B
HEXFET
Æ
MOSFET technology is the key to International
Rectifier's advanced line of power MOSFET transistors. The
efficient geometry design achieves very low on-state re-
sistance combined with high transconductance.
HEXFET
transistors also feature all of the well-established advan-
tages of MOSFETs, such as voltage control, very fast switch-
ing, ease of paralleling and electrical parameter temperature
stability. They are well-suited for applications such as switch-
ing power supplies, motor controls, inverters, choppers,
audio amplifiers, high energy pulse circuits, and virtually
any application where high reliability is required. The
HEXFET
transistor's totally isolated package eliminates the
need for additional isolating material between the device
and the heatsink. This improves thermal efficiency and
reduces drain capacitance.
o
C
A
POWER MOSFET
THRU-HOLE (TO-254AA)
4/17/01
www.irf.com
1
1000V, N-CHANNEL
HEXFET
Æ
MOSFET TECHNOLOGY
TO-254AA
Product Summary
Part Number R
DS(on)
I
D
IRFMG50
2.0
5.6A
Features:
n
Simple Drive Requirements
n
Ease of Paralleling
n
Hermetically Sealed
n
Electrically Isolated
n
Ceramic Eyelets
For footnotes refer to the last page
IRFMG50
IRFMG50
2
www.irf.com
Electrical Characteristics
@ Tj = 25∞C (Unless Otherwise Specified)
Parameter
Min
Typ Max Units
Test Conditions
BVDSS
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage
1000
--
--
V
VGS = 0V, ID = 1.0mA
BVDSS/
TJ Temperature Coefficient of Breakdown
--
1.4
--
V/∞C
Reference to 25∞C, ID = 1.0mA
Voltage
RDS(on)
Static Drain-to-Source On-State
--
--
2.0
VGS = 10V, ID = 3.5A
Resistance
VGS(th)
Gate Threshold Voltage
2.0
--
4.0
V
VDS = VGS, ID = 250µA
gfs
Forward Transconductance
5.2
--
--
S (
)
VDS > 15V, IDS = 3.5A
IDSS
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current
--
--
25
VDS= 800V ,VGS=0V
--
--
250
VDS = 800V,
VGS = 0V, TJ = 125∞C
IGSS
Gate-to-Source Leakage Forward
--
--
100
VGS = 20V
IGSS
Gate-to-Source Leakage Reverse
--
--
-100
VGS = -20V
Qg
Total Gate Charge
--
--
200
VGS =10V, ID =5.6A
Qgs
Gate-to-Source Charge
--
--
20
nC
VDS = 400V
Qgd
Gate-to-Drain (`Miller') Charge
--
--
--
td
(on)
Turn-On Delay Time
--
--
30
VDD = 400V, ID = 5.6A,
tr
Rise Time
--
--
44
RG = 2.35
td
(off)
Turn-Off Delay Time
--
--
210
tf
Fall Time
--
--
60
LS + LD
Total Inductance
--
6.8
--
Ciss
Input Capacitance
--
2400
--
VGS = 0V, VDS = 25V
Coss
Output Capacitance
--
240
--
pF
f = 1.0MHz
Crss
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
--
80
--
CDC
Drain-to-Case Capacitance
--
12
--
nA
nH
ns
µ
A
For footnotes refer to the last page
Thermal Resistance
Parameter
Min Typ Max
Units
Test Conditions
RthJC
Junction-to-Case
--
--
0.83
RthCS
Case-to-sink
--
0.21
--
RthJA
Junction-to-Ambient
--
--
48
Typical socket mount
∞C/W
Source-Drain Diode Ratings and Characteristics
Parameter
Min Typ Max Units
Test Conditions
IS
Continuous Source Current (Body Diode)
--
--
5.6
ISM
Pulse Source Current (Body Diode)
--
--
22
VSD
Diode Forward Voltage
--
--
1.8
V
T
j
= 25∞C, IS = 5.6A, VGS = 0V
trr
Reverse Recovery Time
--
--
1200
nS
Tj = 25∞C, IF = 5.6A, di/dt
100A/
µ
s
QRR Reverse Recovery Charge
--
--
8.4
µC
VDD
50V
ton
Forward Turn-On Time
Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible. Turn-on speed is substantially controlled by LS + LD.
A
Measured from Drain lead (6mm /0.25in. from
package) to Source lead (6mm /0.25in. from
package)

www.irf.com
3
IRFMG50
Fig 4. Normalized On-Resistance
Vs. Temperature
Fig 2. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics
IRFMG50
4
www.irf.com
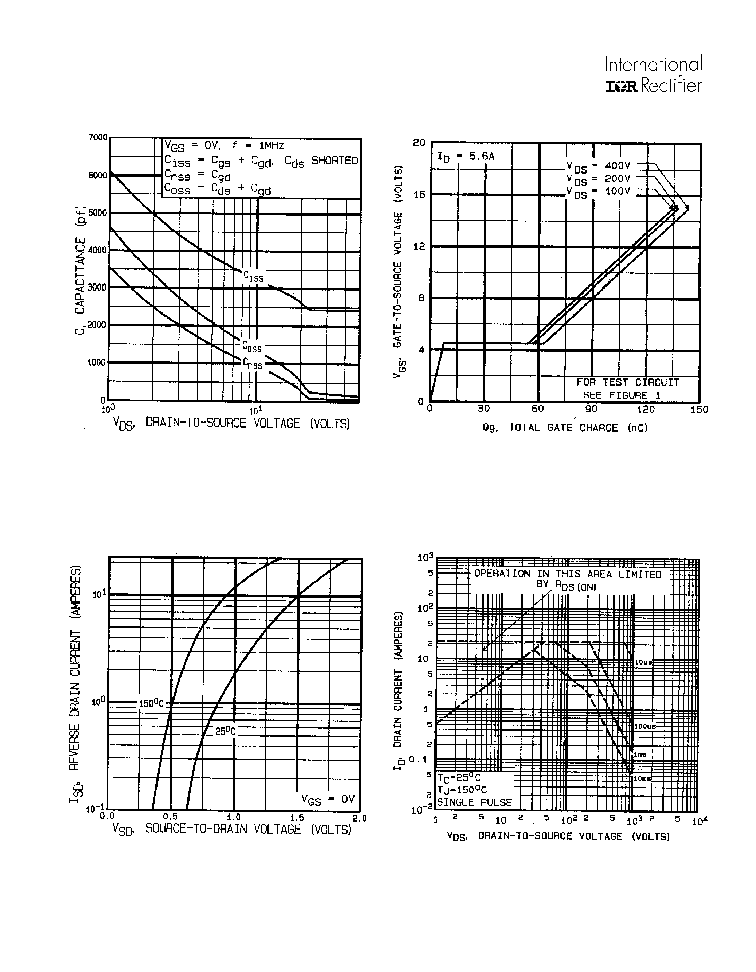
Fig 8. Maximum Safe Operating Area
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge Vs.
Gate-to-Source Voltage
Fig 5. Typical Capacitance Vs.
Drain-to-Source Voltage
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
Forward Voltage
3

www.irf.com
5
IRFMG50
Fig 10a. Switching Time Test Circuit
V
DS
90%
10%
V
GS
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
Fig 10b. Switching Time Waveforms
V
DS
Pulse Width
1
µs
Duty Factor
0.1 %
R
D
V
GS
R
G
D.U.T.
10V
+
-
V
DD
Fig 11. Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case
Fig 9. Maximum Drain Current Vs.
Case Temperature




