The RF Power MOS Line
Power Field Effect Transistor
N≠Channel Enhancement Mode
Designed primarily for linear large≠signal output stages to 80 MHz.
∑
Specified 50 Volts, 30 MHz Characteristics
Output Power = 600 Watts
Power Gain = 21 dB (Typ)
Efficiency = 45% (Typ)
MAXIMUM RATINGS
Rating
Symbol
Value
Unit
Drain≠Source Voltage
V
DSS
125
Vdc
Drain≠Gate Voltage
V
DGO
125
Vdc
Gate≠Source Voltage
V
GS
±
40
Vdc
Drain Current -- Continuous
I
D
60
Adc
Total Device Dissipation @ T
C
= 25
∞
C
Derate above 25
∞
C
P
D
1350
7.7
Watts
W/
∞
C
Storage Temperature Range
T
stg
≠65 to +150
∞
C
Operating Junction Temperature
T
J
200
∞
C
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Characteristic
Symbol
Max
Unit
Thermal Resistance, Junction to Case
R
JC
0.13
∞
C/W
NOTE -- CAUTION -- MOS devices are susceptible to damage from electrostatic charge. Reasonable precautions in handling and
packaging MOS devices should be observed.
MRF157
600 W, to 80 MHz
MOS LINEAR
RF POWER FET
CASE 368≠03, STYLE 2
D
G
S
Order this document
by MRF157/D
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
1
REV 1

ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(T
C
= 25
∞
C unless otherwise noted)
Characteristic
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
OFF CHARACTERISTICS
Drain≠Source Breakdown Voltage (V
GS
= 0, I
D
= 100 mA)
V
(BR)DSS
125
--
--
Vdc
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current (V
DS
= 50 V, V
GS
= 0)
I
DSS
--
--
20
mAdc
Gate≠Body Leakage Current (V
GS
= 20 V, V
DS
= 0)
I
GSS
--
--
5.0
µ
Adc
ON CHARACTERISTICS
Gate Threshold Voltage (V
DS
= 10 V, I
D
= 100 mA)
V
GS(th)
1.0
3.0
5.0
Vdc
Drain≠Source On≠Voltage (V
GS
= 10 V, I
D
= 40 A)
V
DS(on)
1.0
3.0
5.0
Vdc
Forward Transconductance (V
DS
= 10 V, I
D
= 20 A)
g
fs
16
24
--
mhos
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Input Capacitance
(V
DS
= 50 V, V
GS
= 0 V, f = 1.0 MHz)
C
iss
--
1800
--
pF
Output Capacitance
(V
DS
= 50 V, V
GS
= 0, f = 1.0 MHz)
C
oss
--
750
--
pF
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
(V
DS
= 50 V, V
GS
= 0, f = 1.0 MHz)
C
rss
--
75
--
pF
FUNCTIONAL TESTS
Common Source Amplifier Power Gain
(V
DD
= 50 V, P
out
= 600 W, I
DQ
= 800 mA, f = 30 MHz)
G
ps
15
21
--
dB
Drain Efficiency
(V
DD
= 50 V, P
out
= 600 W, f = 30 MHz, I
DQ
= 800 mA)
h
40
45
--
%
Intermodulation Distortion
(V
DD
= 50 V, P
out
= 600 W(PEP), f1 = 30 MHz,
f2 = 30.001 MHz, I
DQ
= 800 mA)
IMD
(d3)
--
≠25
--
dB
Figure 1. 30 MHz Test Circuit
C1, C3, C8 -- Arco 469
C2 -- 330 pF
C4 -- 680 pF
C5, C19, C20 -- 0.47
µ
F, RMC Type 2225C
C6, C7, C14, C15, C16 -- 0.1
µ
F
C9, C10, C11 -- 470 pF
C12 -- 1000 pF
C13 -- Two Unencapsulated 1000 pF Mica, in Series
C17, C18 -- 0.039
µ
F
C21 -- 10
µ
F/100 V Electrolytic
L1 -- 2 Turns #16 AWG, 1/2
ID, 3/8
Long
L2, L3 -- Ferrite Beads, Fair≠Rite Products Corp. #2673000801
R1, R2 -- 10 Ohms/2W Carbon
T1 -- RF Transformer, 1:25 Impedance Ratio. See M/A-COM
T1 --
Application Note AN749, Figure 4 for details.
T1 --
Ferrite Material: 2 Each, Fair≠Rite Products
T1 --
Corp. #2667540001
All capacitors ATC type 100/200 chips or equivalent unless otherwise noted.
0-6 V
R1
C5
C6
R2
C4
L1
C1
C2
C3
C7
RF
INPUT
+
-
D.U.T.
C9
C10 C11 C12 C13
C14
C15 C16 C17 C18
C19
C8
T1
L2
L3
C20 C21
50 V
+
-
RF
OUTPUT
+
2
REV 1

C1 -- 1000 pF Ceramic Disc Capacitor
C2, C3, C4 -- 0.1
µ
F Ceramic Disc Capacitor
C5 -- 0.01
µ
F Ceramic Chip Capacitor
C6, C12 -- 0.1
µ
F Ceramic Chip Capacitor
C7, C8 -- Two 2200 pF Ceramic Chip Capacitors in Parallel
C7, C8 --
Each
C9 -- 820 pF Ceramic Chip Capacitor
C10, C11 -- 1000 pF Ceramic Chip Capacitor
C13 -- 0.47
µ
F Ceramic Chip Capacitor or Two Smaller
C13 --
Values in Parallel
C14 -- Unencapsulated Mica, 500 V. Two 1000 pF Units
C14 --
in Series, Mounted Under T2
D1 -- 1N5357A or Equivalent
D2, D3 -- 1N4148 or Equivalent.
IC1 -- MC1723 (723) Voltage Regulator
L1, L2 -- 15
H, Connecting Wires to R14 and R15,
L1, L2 --
2.5 cm Each #20 AWG
Figure 11. 2.0 to 50 MHz, 1.0 kW Wideband Amplifier
L3 -- 10
µ
H, 10 Turns #12 AWG Enameled Wire on
L3 --
Fair≠Rite Products Corp. Ferrite Toroid #5961000401 or Equivalent
R1, R2 -- 1.0K Single Turn Trimpots
R3 -- 10K Single Turn Trimpot
R4 -- 470 Ohms, 2.0 Watts
R5 -- 10 Ohms
R6, R12, R13 -- 2.0K Ohms
R7 -- 10K Ohms
R8 -- Exact Value Depends on Thermistor R9 used
R8 --
(Typically 5.0≠10K)
R9 -- Thermistor, Keystone RL1009≠5820≠97≠D1 or
R9 --
Equivalent
R10, R11 -- 100 Ohms, 1.0W Carbon
R14, R15 -- EMC Technology Model 5308 or KDI
R14, R15 --
Pyrofilm PPR 870≠150≠3 Power Resistors,
R14, R15 --
25 Ohms
T1, T2 -- 9:1 and 1:9 Impedance Ratio RF Transformers
Unless otherwise noted, all resistors are 1/2 watt metal film type. All chip capacitors except C13 are ATC type 100/200B or Dielectric Laboratories type C17.
R1
D2
R10
C3
R12
C7
R14
22pF
C9
T1
L2
L1
C8
R15
C14
D3
R11
R2
R6
C4
R13
R5
R7
R8
R9
C2
T2
C13
L3
50 V
+
-
OUTPUT
C10
C11
C12
D.U.T
.
D.U.T.
BIAS 36-50 V
-
+
R4
D1
C1 R3
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
13
11
12
L2
RF POWER MOSFET CONSIDERATIONS
MOSFET CAPACITANCES
The physical structure of a MOSFET results in capacitors
between the terminals. The metal oxide gate structure deter-
mines the capacitors from gate≠to≠drain (C
gd
), and gate≠to≠
source (C
gs
). The PN junction formed during the fabrication
of the TMOS
Æ
FET results in a junction capacitance from
drain≠to≠source (C
ds
).
These capacitances are characterized as input (C
iss
), out-
put (C
oss
) and reverse transfer (C
rss
) capacitances on data
sheets. The relationships between the interterminal capaci-
tances and those given on data sheets are shown below. The
C
iss
can be specified in two ways:
1. Drain shorted to source and positive voltage at the gate.
2. Positive voltage of the drain in respect to source and zero
volts at the gate. In the latter case the numbers are lower.
However, neither method represents the actual operat-
ing conditions in RF applications.
GATE
DRAIN
SOURCE
C
ds
C
gs
C
gd
C
iss
= C
gd
+ C
gs
C
oss
= C
gd
+ C
ds
C
rss
= C
gd
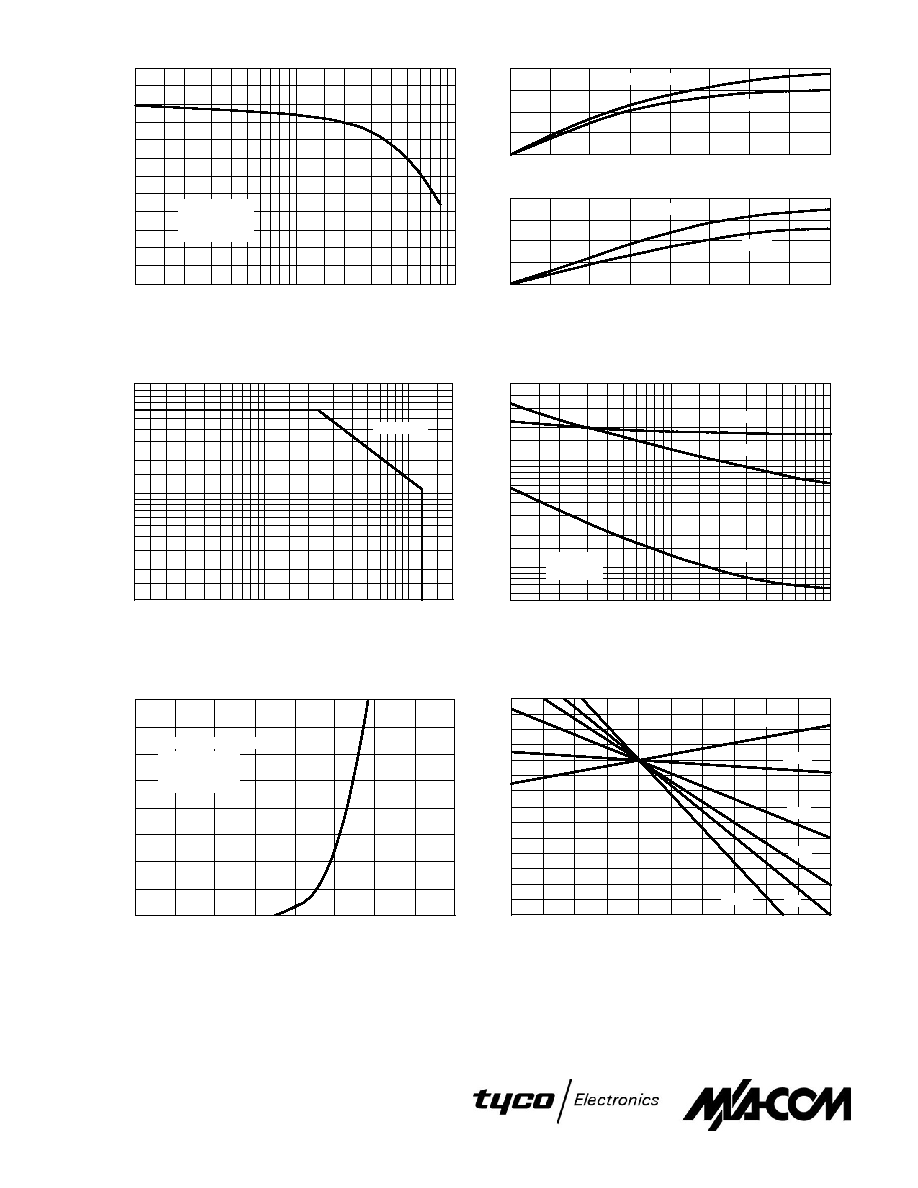
LINEARITY AND GAIN CHARACTERISTICS
In addition to the typical IMD and power gain data pres-
ented, Figure 5 may give the designer additional information
on the capabilities of this device. The graph represents the
small signal unity current gain frequency at a given drain cur-
rent level. This is equivalent to f
T
for bipolar transistors.
Since this test is performed at a fast sweep speed, heating of
the device does not occur. Thus, in normal use, the higher
temperatures may degrade these characteristics to some ex-
tent.
DRAIN CHARACTERISTICS
One figure of merit for a FET is its static resistance in the
full≠on condition. This on≠resistance, V
DS(on)
, occurs in the
linear region of the output characteristic and is specified un-
der specific test conditions for gate≠source voltage and drain
current. For MOSFETs, V
DS(on)
has a positive temperature
coefficient and constitutes an important design consideration
at high temperatures, because it contributes to the power
dissipation within the device.
GATE CHARACTERISTICS
The gate of the TMOS FET is a polysilicon material, and is
electrically isolated from the source by a layer of oxide. The
input resistance is very high -- on the order of 10
9
ohms --
resulting in a leakage current of a few nanoamperes.
Gate control is achieved by applying a positive voltage
slightly in excess of the gate≠to≠source threshold voltage,
V
GS(th)
.
5
REV 1