 | –≠–Ľ–Ķ–ļ—ā—Ä–ĺ–Ĺ–Ĺ—č–Ļ –ļ–ĺ–ľ–Ņ–ĺ–Ĺ–Ķ–Ĺ—ā: CXD1852Q | –°–ļ–į—á–į—ā—Ć:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Description
The CXD1852Q is a single-chip MPEG1 decoder
with a built-in CD-ROM decoder which allows
decoding of MPEG1 system, video and audio layers.
A built-in CD-ROM decoder enables direct connection
with a CD-DSP. Combining this chip with a control
microcomputer and 4-Mbit DRAM, etc. allows
configuration of a MPEG1 decoding system for video
CD players, etc.
Features
∑ Supply voltage: 3.3 Ī 0.3V
∑ Input and output voltages: LVTTL compatible
∑ 5V can be applied as the input voltage (excluding
some pins)
∑ Allows decoding of MPEG1 system, video and
audio layers
∑ Built-in CD-ROM decoder allows direct connection
with a CD-DSP
∑ CD-ROM decoded output can be transferred to
and stored in an external DRAM
∑ RGB and YCbCr video data output allowed
∑ Built-in video sync generator
∑ Audio data output can support various DAC
∑ Supports various special playback modes
∑ Video CD PAL high resolution still picture can be
decoded with a single 4-Mbit DRAM
∑ 8-bit parallel and 4-line serial host interfaces
∑ CD-DA through operation allowed
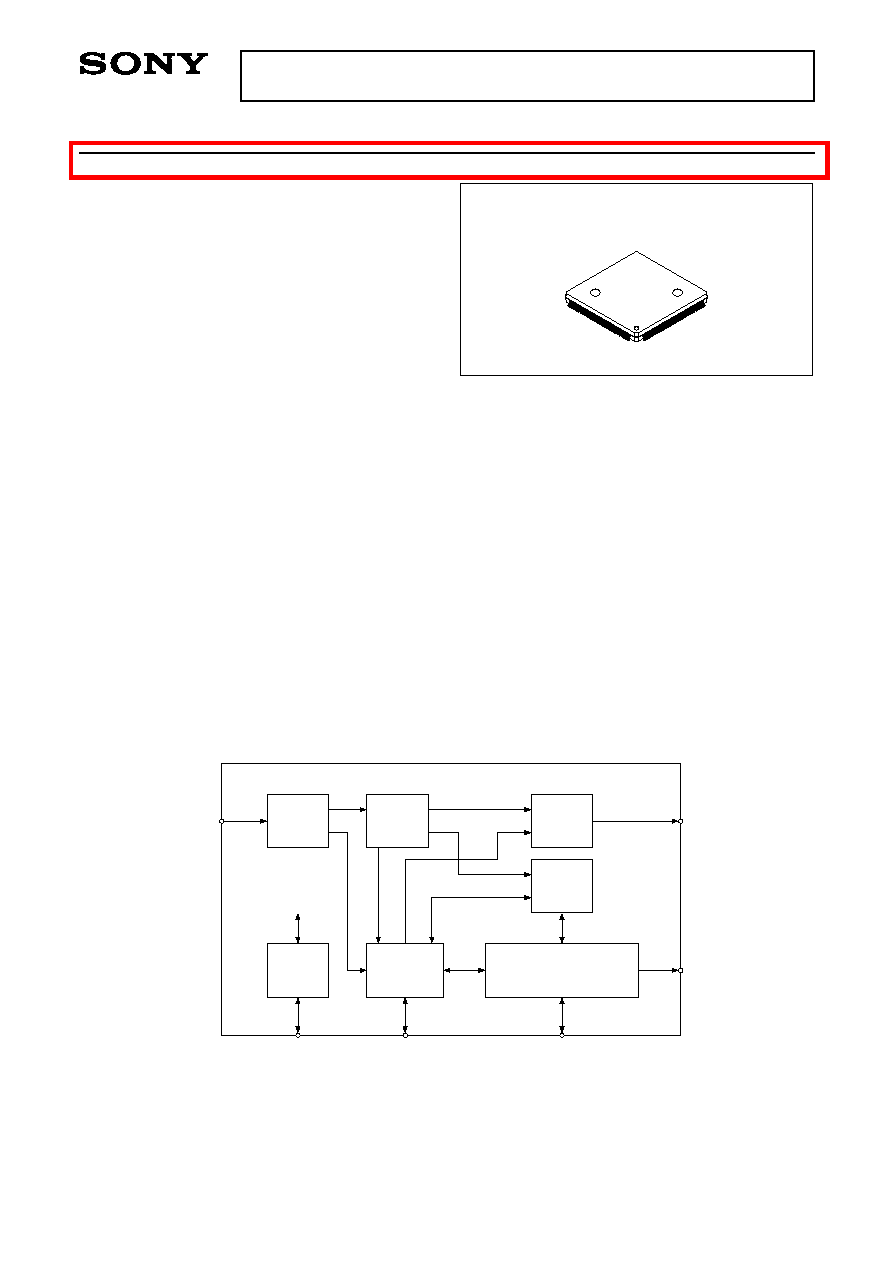
Block Diagram
Structure
Silicon gate CMOS IC
Applications
Video CD players, MPEG1 decoder boards, etc.
≠ 1 ≠
CXD1852Q
E96656-PS
MPEG1 Decoder
Sony reserves the right to change products and specifications without prior notice. This information does not convey any license by
any implication or otherwise under any patents or other right. Application circuits shown, if any, are typical examples illustrating the
operation of the devices. Sony cannot assume responsibility for any problems arising out of the use of these circuits.
120 pin QFP (Plastic)
CD-ROM
Decoder
MPEG
System
Decoder
MPEG
Audio
Decoder
MPEG
Video
Decoder
Video Postprocessor
&
Sync Generator
DRAM
Controler
Host
interface
To each circuit block
Audio
I/F
Video
I/F
CD-DSP
I/F
Host
I/F
DRAM
I/F
Video Sync
Signal
For the availability of this product, please contact the sales office.
≠ 2 ≠
CXD1852Q
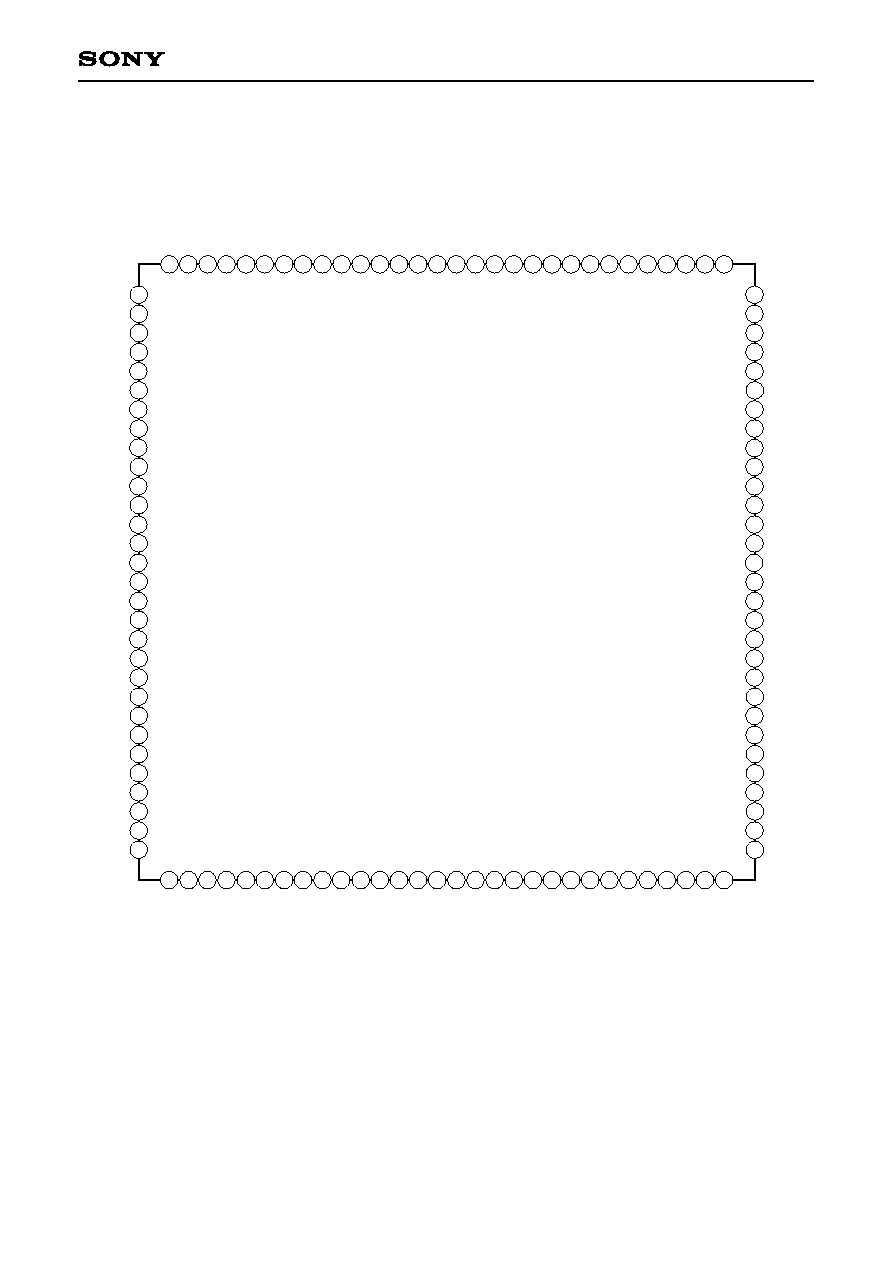
1. Pin Configuration
V
SS
XTL0O
XTL0I
V
DD
HA2
HA3
HD0
HD1
HD2
HD3
HD4
HD5
HD6
V
DD
V
SS
HD7
MA3
MA4
MA2
MA5
MA1
V
SS
MA6
MA0
BC
TCKI
TDI
TENA1
TDO
VST
V
DD
DCLK
B/Cb7
B/Cb6
B/Cb5
B/Cb4
B/Cb3
B/Cb2
B/Cb1
B/Cb0
G/Y7
G/Y6
G/Y5
G/Y4
G/Y3
V
SS
V
DD
G/Y2
G/Y1
G/Y0
R/Cr7
R/Cr6
R/Cr5
R/Cr4
R/Cr3
R/Cr2
R/Cr1
R/Cr0
XVOE
V
SS
V
SS
MA7
MA8
XRAS
XMWE
XCAS2/MA9
XCAS0
MD7
MD8
MD6
MD9
MD5
MD10
V
DD
V
SS
MD4
MD11
MD3
MD12
MD2
MD13
MD1
MD14
MD0
MD15
OSDEN
OSDB
OSDG
OSDR
V
DD
HA1
HA0
XRST
XHIRQ
HRW
XHDT
XHCS
DOIN
BCKI
DATI
LRCI
C2PO
V
DD
XTL2I
XTL2O
V
SS
V
DD
FSXI
BCKO
LRCO
DATO
DOUT
CLK0O
XSGRST
CSYNC
CBLNK/FSC
FID/FHREF
VSYNC
HSYNC
V
SS
100 99 98 97 96 95 94
91
92
93
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
31 32 33
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
1
70
69
68
67
63
64
65
66
61
62
71
72
73
74
81
82
83
84
75
76
77
78
88
87
86
85
79
80
89
90
≠ 3 ≠
CXD1852Q
2. Pin Description
+3.3V power supply
Connect to ground.
Video decoder master clock. Input the clock to XTL0I or connect an
oscillator between XTL0I and XTL0O. The recommended frequencies are
27MHz, 28.6363MHz (NTSC 8fsc) and 35.4686MHz (PAL 8fsc).
When the host interface operates in parallel mode, these pins are the
register address inputs. In serial mode, HA0 is the serial data input, and
HA1 to HA3 should be fixed to low level.
When the host interface operates in parallel mode, these pins are the
register data I/Os. In serial mode, HD0 is the serial data output, and HD1
to HD7 should be fixed to low level.
DRAM address signal outputs. Connect to the DRAM address pins so that
the numbers match.
Row address strobe signal output. Connect to the DRAM RAS signal pin.
DRAM write enable signal output. Connect to the DRAM WE signal pin.
Used when connecting 8 Mbits of DRAM. Connect to the upper word
(256K to 512K-1) DRAM CAS signal pin (for both the upper and lower
bytes) when the DRAM configuration is 256 Kwords
◊
16 bits
◊
2, and to
the MA9 pin (for two DRAMs) when the DRAM configuration is 512 Kwords
◊
8 bits
◊
2.
DRAM column address strobe signal output. Connect to the lower word
(0 to 256K-1) DRAM CAS signal pin (for both the upper and lower bytes)
when the DRAM configuration is 256Kwords
◊
16 bits
◊
2, and to all
DRAM CAS signal pins in all other cases.
DRAM data signal I/Os. Connect to the DRAM data pins so that the
numbers match.
OSD enable signal. The enabled polarity is changed by the register
settings.
OSD data inputs. When the signal input to the OSDEN pin is enabled, the
color registered in the color table which is specified by these three inputs
(3 bits) is output as the image data.
Video output enable signal. Image data output and DCLK output are
enabled when this pin is low, and disabled when this pin is high (high
impedance). Note that the output control register must be set to output
enable for output to be enabled.
Image data outputs. The output data format (RGB, YCbCr, etc.) and the
correspondence between the pins and output data can be changed by
setting the registers.
Dot clock (DCLK) signal. The DCLK frequency is normally 13.5MHz.
DCLK can be input from this pin, or frequency divided from the clock input
and output from this pin.
2
3
5, 6, 119,
120
7 to 13,
16
17 to 21,
23, 24,
32, 33
34
35
36
37
38 to 43,
46 to 55
56
57 to 59
62
63 to 70
71 to 73,
76 to 88
81 to 88
89
V
DD
V
SS
XTL0O
XTL0I
HA0 to HA3
HD0 to HD7
MA0 to MA8
XRAS
XMWE
XCAS2/
MA9
XCAS0
MD0 to
MD15
OSDEN
OSDB,
OSDG,
OSDR
XVOE
R/Cr0 to
R/Cr7
G/Y0 to
G/Y7
B/Cb0 to
B/Cb7
DCLK
O
I
I
I/O
O
O
O
O
O
I/O
I
I
I
O
I/O
Pin No.
Symbol
I/O
Description
≠ 4 ≠
CXD1852Q
Horizontal sync signal. When using the built-in sync generator, the dot
clock (DCLK) is frequency divided and output. When not using the sync
generator, this pin is an input.
Vertical sync signal. When using the built-in sync generator, the dot clock
(DCLK) is frequency divided and output. When not using the built-in sync
generator, this pin is an input.
Field identification signal (FID) and horizontal sync phase reference signal
(FHREF). The signal to be used is set in the register. When set to FID, this
pin is an output if using the built-in sync generator, and an input if not
using the built-in sync generator. High corresponds to odd fields. When set
to FHREF, this pin outputs the signal obtained by frequency dividing XTL0.
When XTL0 is 8fsc, this signal is equivalent to the HSYNC cycle, and can
be used for phase comparison with the HSYNC signal.
Composite blanking signal (CBLNK) and fsc signal. The signal to be used
is set in the register. When set to CBLNK, this pin is an output if using the
built-in sync generator, and an input if not using the built-in sync generator.
When set to fsc, this pin outputs the signal obtained by frequency dividing
XTL0. The frequency division ratio can be selected from 1/8 or 1/16.
Composite sync signal obtained by frequency dividing DCLK. This pin
cannot be input.
Sync generator reset signal input. The built-in sync generator is initialized
by setting this pin low.
Output for clock obtained by frequency dividing XTL0. The frequency
division ratio can be selected from 1, 1/2, 1/4 or 1/8.
Audio digital output.
Audio serial data output to DAC.
L/R clock output to DAC.
Bit clock output to DAC.
Audio interface clock input. Input 256fs (11.2896MHz), 384fs
(16.9344MHz), 512fs (22.5792MHz), or 768fs (33.8688MHz), etc.
Master clock for CD-ROM and audio decoders. Input the clock to XTL2I or
connect an oscillator between XTL2I and XTL2O. The recommended
frequency is 45MHz. Note that this clock is for the internal circuits, and the
input and output are not synchronized.
C2 pointer input from CD-DSP. Indicates that the DATI input contains an
error.
LR clock input from CD-DSP. Indicates the L or R channel of DATI.
Serial data input from CD-DSP.
Bit clock input from CD-DSP. This clock strobes the DATI input.
Digital data input from CD-DSP.
Chip select signal input during register access.
Wait signal output during register access. This pin is valid only when the
host interface operates in parallel mode. This pin functions as an open
drain, and should therefore be pulled up. It should be pulled up when the
host interface operates in serial mode as well.
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
106
107
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
HSYNC
VSYNC
FID/FHREF
CBLNK/
FSC
CSYNC
XSGRST
CLK0O
DOUT
DATO
LRCO
BCKO
FSXI
XTL2O
XTL2I
C2PO
LRCI
DATI
BCKI
DOIN
XHCS
XHDT
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I
O
O
O
O
O
I
O
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I/O
Pin No.
Symbol
I/O
Description

≠ 5 ≠
CXD1852Q
R/W signal input when the host interface operates in parallel mode. Serial
clock input in serial mode.
Interrupt request signal output. This pin functions as an open drain, and
should therefore be pulled up.
Hardware reset signal input. All operation is initialized by setting this pin
low.
Test. Leave open.
Test. Leave open.
Test. Leave open.
Test. Leave open.
Test. Leave open.
Test. Connect to ground.
116
117
118
25
26
27
28
29
30
HRW
XHIRQ
XRST
BC
TCKI
TDI
TENA1
TDO
VST
I
O
I
--
--
--
--
--
--
Pin No.
Symbol
I/O
Description
≠ 6 ≠
CXD1852Q
3. Electrical Characteristics
3-1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
(Ta = 25įC, V
SS
= 0V)
Item
Supply voltage
Input pin voltage
Input pin voltage
Output pin voltage
Output pin voltage
I/O pin voltage
Allowable power dissipation
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
V
DD
V
I
V
I
V
O
V
O
V
I/O
P
D
Topr
Tstg
≠0.5 to +4.6
≠0.5 to V
DD
+ 0.5
≠0.5 to +5.5
≠0.5 to V
DD
+ 0.5
≠0.5 to +5.5
≠0.5 to +5.5
1.0
≠20 to +75
≠55 to +150
V
V
V
V
V
V
W
įC
įC
1
2
3
4
Symbol
Rating
Unit
Remarks
1
XTL0I and XTL2I pins
2
Input pins other than those in
1
above.
3
XTL0O and XTL2O pins
4
Output pins other than those in
3
above.
3-2. Recommended Operating Conditions
(Ta = ≠20 to +75įC, V
SS
= 0V)
Item
Supply voltage
High level input voltage
High level input voltage
Low level input voltage
Input rise time
Input fall time
Operating temperature
V
DD
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
Tr
Tf
Topr
3.0
2.2
2.2
0
0
0
≠20
V
V
V
V
ns
ns
įC
1
2
Symbol
Min.
3.3
--
--
--
--
--
--
Typ.
3.6
V
DD
5.0
0.8
50
50
75
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
XTL0I and XTL2I pins
2
I/O pins and input pins other than those in
1
above.

≠ 7 ≠
CXD1852Q
3-3. DC Characteristics
(Ta = ≠20 to +75įC, V
SS
= 0V, V
DD
= 3.3 Ī 0.3V)
Item
Average operating
supply current
Input leak current
High level output voltage
High level output voltage
Low level output voltage
Low level output voltage
Output leak current
Feedback resistance
Logic threshold value
High level output voltage
Low level output voltage
I
DD
I
I
V
OH
V
OH
V
OL
V
OL
I
OZ
R
FB
LVth
V
OH
V
OL
--
≠40
V
DD
≠ 0.8
--
--
--
≠40
250k
--
V
DD
/2
--
mA
ĶA
V
V
V
V
ĶA
V
V
V
1
2
2
2
2
2
3
4
5
5
Symbol
V
I
= 0 to 5.0V
I
OH
= ≠2mA
I
OH
= ≠100ĶA
I
OL
= 4mA
I
OL
= 100ĶA
V
O
= 0 to 5.0V,
output disabled status
V
I
= 0V or V
I
= V
DD
I
OH
= ≠12mA
I
OL
= 12mA
Measurement conditions
Min.
--
--
--
V
DD
≠ 0.4
--
0.04
--
1M
V
DD
/2
--
--
Typ.
100
40
--
--
0.4
--
40
2.5M
--
--
V
DD
/2
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
Input pins other than XTL0I and XTL2I
2
I/O pins and output pins other than XTL0O and XTL2O
3
Oscillators (between XTL0I and XTL0O, and between XTL2I and XTL2O)
4
XTL0I and XTL2I pins
5
XTL0O and XTL2O pins
3-4. Clock Signal AC Characteristics
XTL0I
t
WHX0
t
WLX0
t
CX0
XTL2I
t
WHX2
t
WLX2
t
CX2
Item
XTL0I frequency
XTL0I cycle
XTL0I high level interval
XTL0I low level interval
XTL2I frequency
XTL2I cycle
XTL2I high level interval
XTL2I low level interval
f
X0
t
CX0
t
WHX0
t
WLX0
f
X2
t
CX2
t
WHX2
t
WLX2
--
33.3
10
10
44.7
--
8
8
MHz
ns
ns
ns
MHz
ns
ns
ns
1
1
2
2
Symbol
Min.
--
--
--
--
45.1584
22.2
--
--
Typ.
60
--
--
--
45.4
--
--
--
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
When using in combination with the XTL0O pin as an oscillator, the maximum oscillation frequency is 50MHz.
2
When using in combination with the XTL2O pin as an oscillator, the maximum oscillation frequency is 50MHz.
≠ 8 ≠
CXD1852Q
3-5. Host Interface AC Characteristics
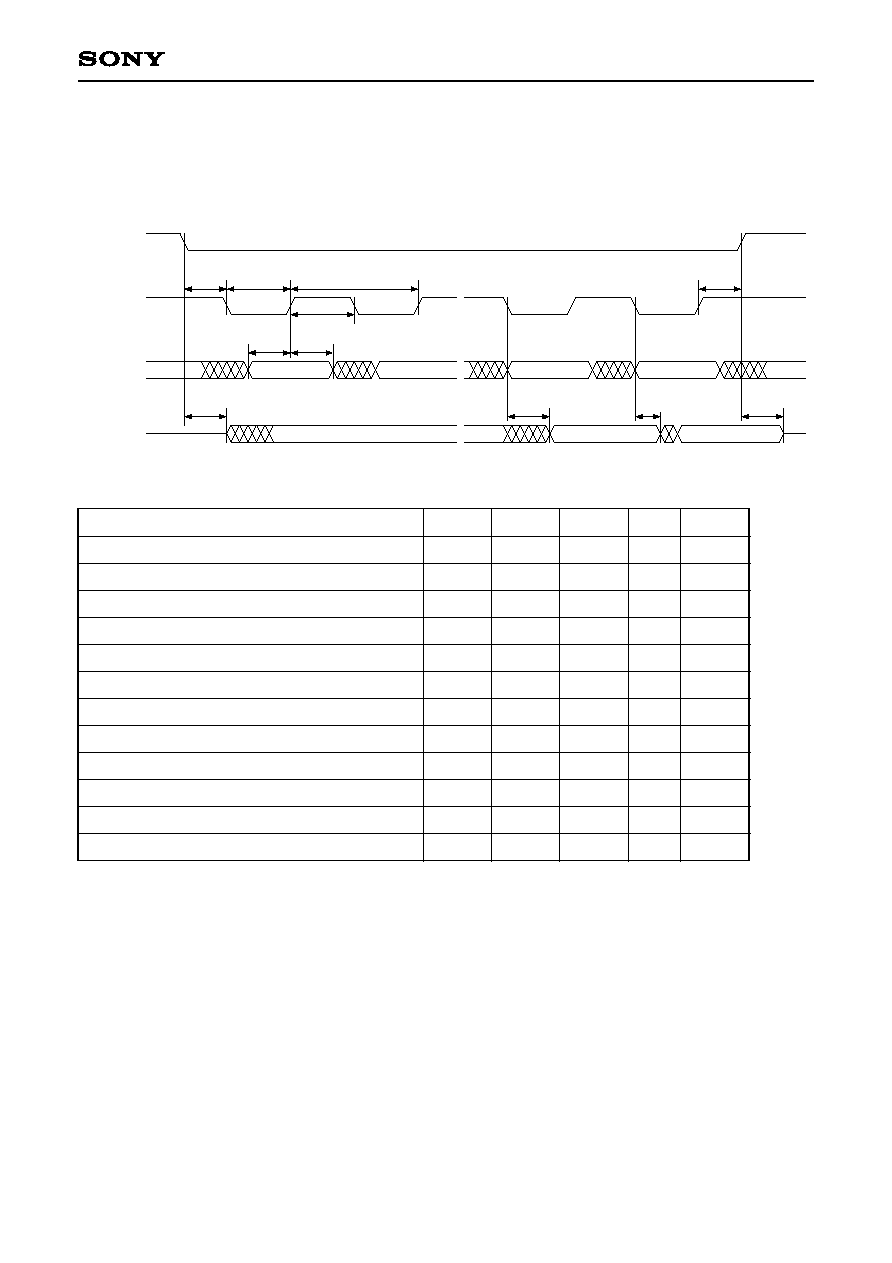
3-5-1. Serial Mode (write, read)
Item
Serial clock frequency
Serial clock cycle
Serial clock high level interval
Serial clock low level interval
Chip select setup time
Chip select hold time
Serial input setup time
Serial input hold time
Serial output enable time
Serial output determination time
Serial output hold time
Serial output disable time
f
SK
t
CSK
t
WHSK
t
WLSK
t
SCS
t
HCS
t
SSI
t
HSI
t
LZSQ
t
DSQ
t
OHSQ
t
HZSQ
--
500
100
100
0
500
30
30
0
--
5
0
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Symbol
Min.
2
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
15
40
--
15
Max.
Unit
Remarks
t
SCS
t
WLSK
t
CSK
t
WHSK
t
SSI
t
HSI
t
HCS
t
HZSQ
t
OHSQ
t
DSQ
t
LZSQ
XHCS
HRW
(SCK)
HA0
(SI)
HD0
(SQ)
≠ 9 ≠
CXD1852Q
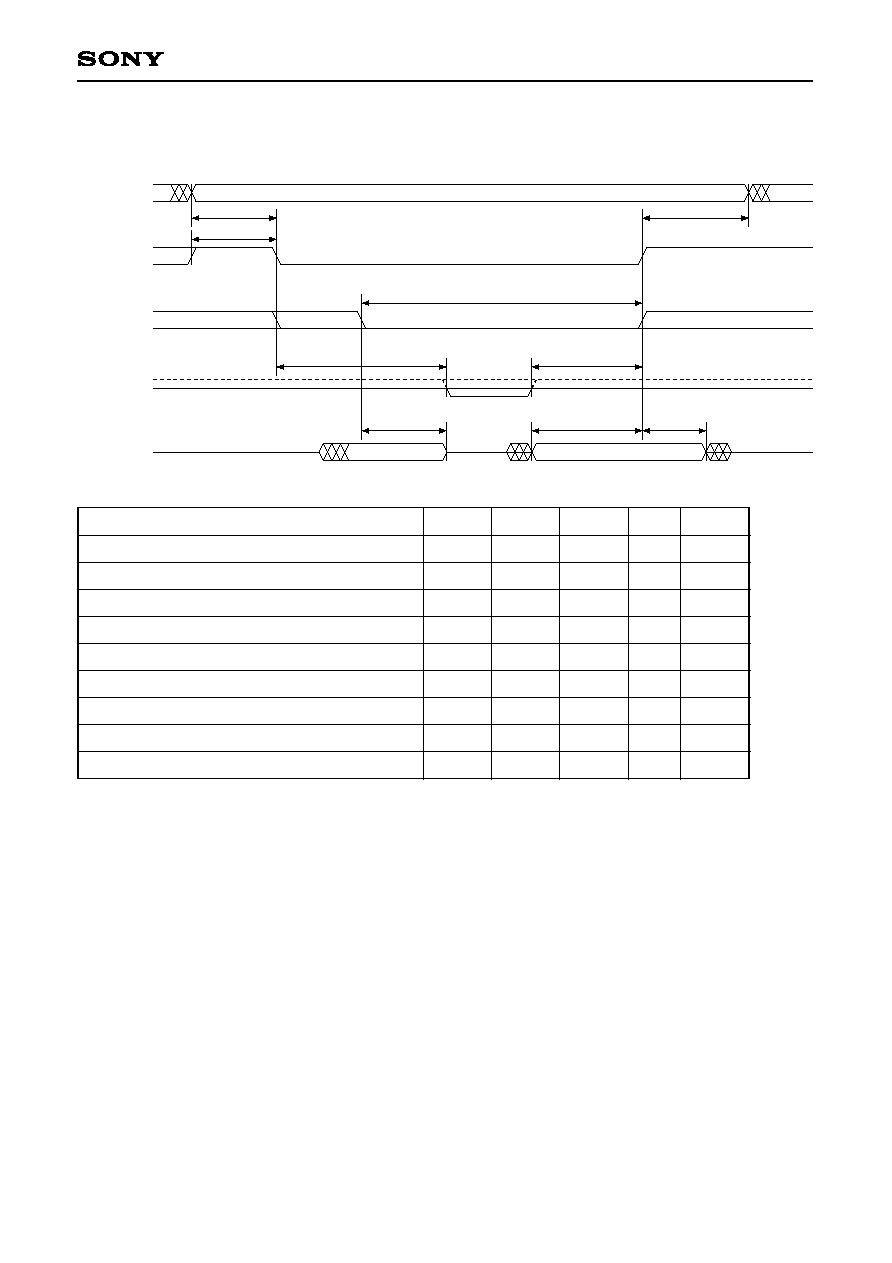
3-5-2. Parallel Mode, Register Write
HA0 to 3
XHCS
XHRW
XHDT
HD0 to 7
t
SA
t
WCSH
t
HA
t
WWL1
t
HW1
t
SD1
t
HD1
t
HZQ2
t
DWA1
input
output
Item
Address setup time
Address hold time
Chip disable time
Write pulse width
Write pulse hold time
Wait signal delay time
HD output disable time (for WR)
HD input setup time
HD input hold time
t
SA
t
HA
t
WCSH
t
WWL1
t
HW1
t
DWA1
t
HZQ2
t
SD1
t
HD1
20
20
20
60
10
--
--
25
25
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
1
2
3
2,
4
1,
4
5
2
2
Symbol
Min.
--
--
--
--
--
15
15
--
--
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
Specified for the edge of XHCS or HRW, whichever is later.
2
Specified for the edge of XHCS or HRW, whichever is earlier.
3
Interval during which both XHCS and HRW are low.
4
Applies only to access resulting in wait status.
5
Do not apply data while output is enabled.
≠ 10 ≠
CXD1852Q
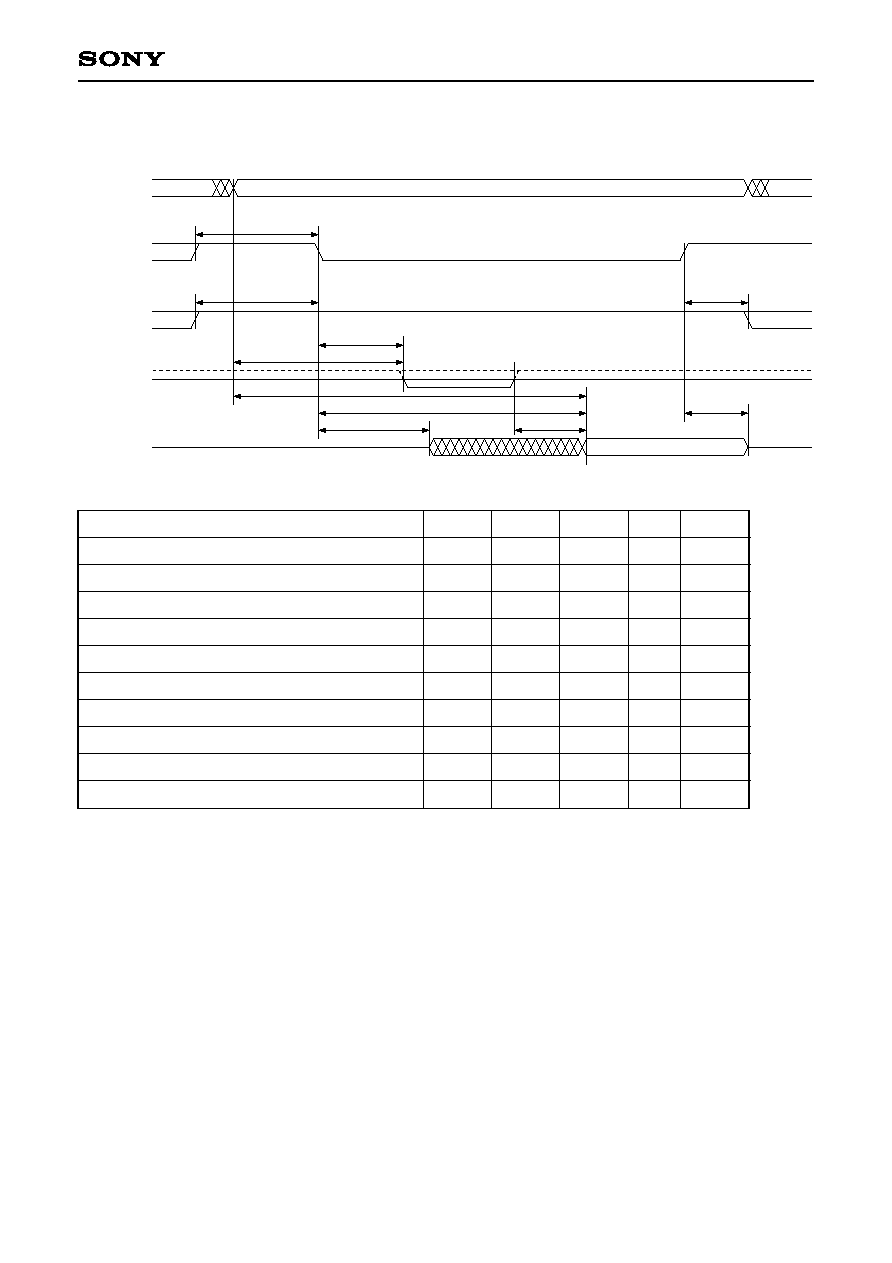
3-5-3. Parallel Mode, Register Read
HA0 to 8
XHCS
(CS)
t
WCSH
valid output
t
SR
HD0 to 7
t
HR
t
DWA3
t
DWA2
t
LZQ1
t
DQ1
t
DQ4
t
DQ2
t
HZQ1
XHRW
(WR)
XHDT
(WAIT)
Item
Chip disable time
Read setup time
Read hold time
Wait signal delay time (for CE)
Wait signal delay time (for HA)
HD output enable time (for CE)
HD output determination time (for CE)
HD output determination time (for HA)
HD output determination time (for WAIT)
HD output disable time (for CE)
t
WCSH
t
SR
t
HR
t
DWA2
t
DWA3
t
LZQ1
t
DQ1
t
DQ2
t
DQ4
t
HZQ1
20
10
10
--
--
0
--
0
--
--
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
1
1
2
3
3
3,
4
Symbol
Min.
--
--
--
15
15
--
60
60
30
15
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
Applies only to access resulting in wait status. XHDT goes low at the later timing of CE or HA.
2
HD output is enabled when both conditions are met.
3
HD output is determined when all conditions are met.
4
Applies only to access resulting in wait status.

≠ 11 ≠
CXD1852Q
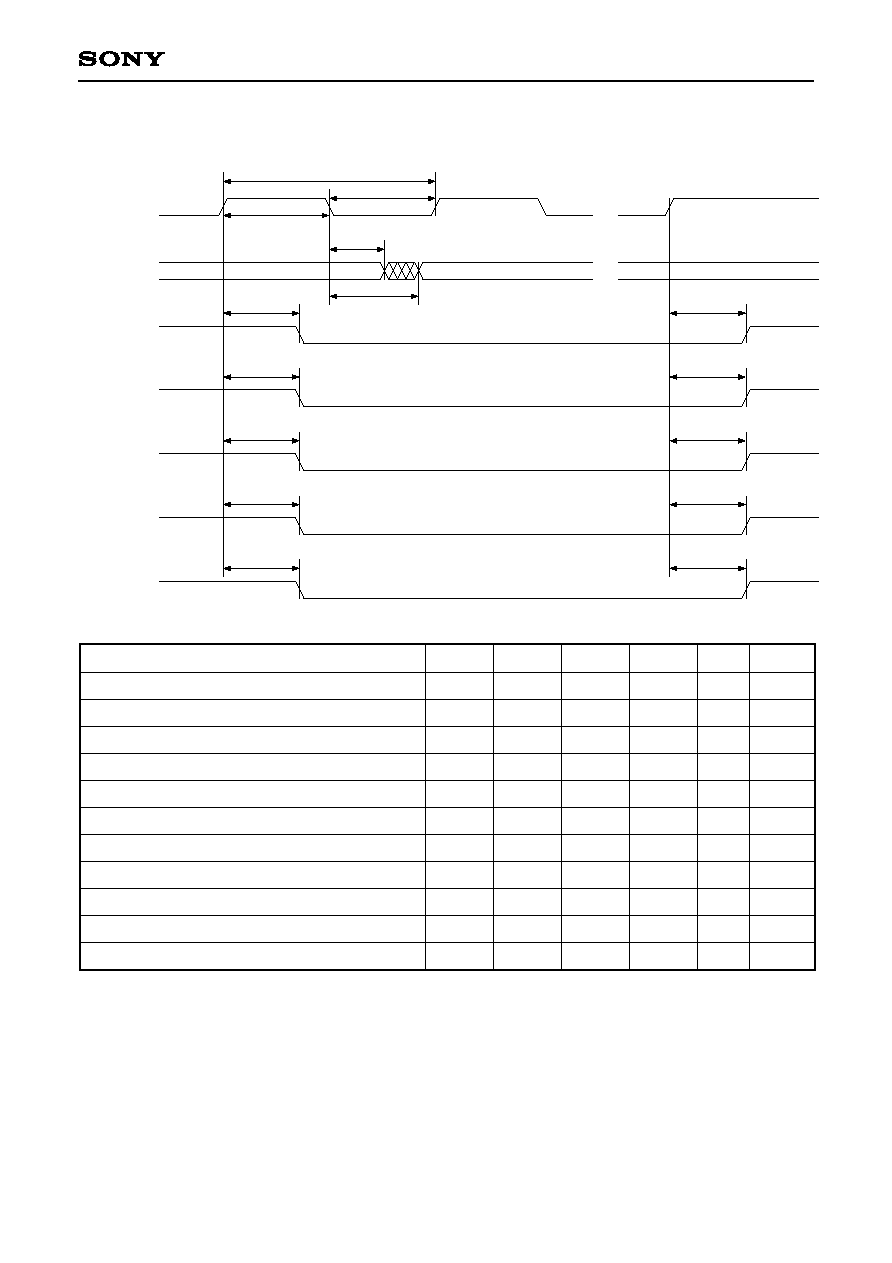
3-6. Interface for CD Signal Processing LSI
BCKFEDG = 0
t
BCKI
t
BCKI
t
SBC2
t
HBC2
t
HBC1
t
SBC1
BCKI
DATI
LRCI, C2PO
t
BCKI
t
BCKI
t
SBC2
t
HBC2
t
HBC1
t
SBC1
BCKI
DATI
LRCI, C2PO
BCKFEDG = 1
Item
BCKI frequency
BCKI pulse width
DATI setting time (for BCKI)
DATI hold time (for BCKI)
LRCI, C2PO setting time (for BCKI)
LRCI, C2PO hold time (for BCKI)
f
BCKI
t
BCKI
t
SBC1
t
HBC1
t
SBC2
t
HBC2
87
20
20
20
20
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Symbol
Min.
5.7
--
--
--
--
--
Max.
Unit
Remarks
≠ 12 ≠
CXD1852Q
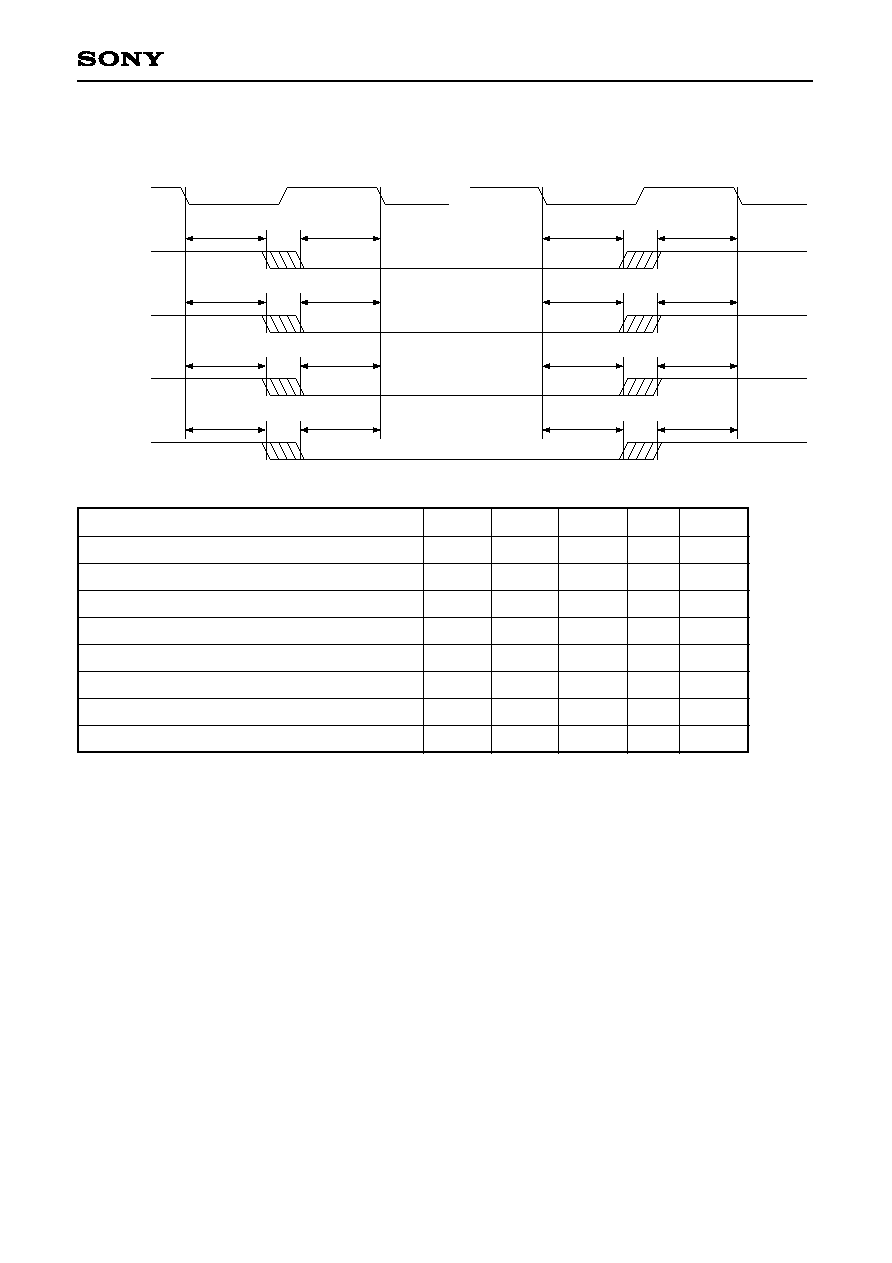
3-7. Image Data Output, Video Sync Signal Output AC Characteristics
t
CDCK
DCLK
R/Cr0 to 7
G/Y0 to 7
B/Cb0 to 7
HSYNC
t
DHSY
t
WLDCK
t
HPD
t
DPD
t
DHSY
t
WHDCK
VSYNC
t
DVSY
CSYNC
t
DCSY
CBLNK
t
DCBL
FID
t
DFID
t
DVSY
t
DCSY
t
DCBL
t
DFID
Item
DCLK frequency
DCLK cycle
DCLK high level interval
DCLK low level interval
Image data output determination time
Image data output hold time
HSYNC output delay time
VSYNC output delay time
CSYNC output delay time
CBLNK output delay time
FID output delay time
f
DCK
t
CDCK
t
WHDCK
t
WLDCK
t
DPD
t
HPD
t
DHSY
t
DVSY
t
DCSY
t
DCBL
t
DFID
--
--
--
--
--
0
--
--
--
--
--
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
1
1
1
1
1,
2
1,
2
1
1
1
1
1
Symbol
Min.
13.5
74.1
37
37
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
Typ.
--
--
--
--
15
--
30
30
30
30
30
Max.
Unit Remarks
1
When both inputting and outputting DCLK. For output, a load of 75pF is connected to DCLK.
2
The chart shows the case where the pixel data output is synchronized to the fall of DCLK, but is also the
same when synchronized to the rise of DCLK.
≠ 13 ≠
CXD1852Q
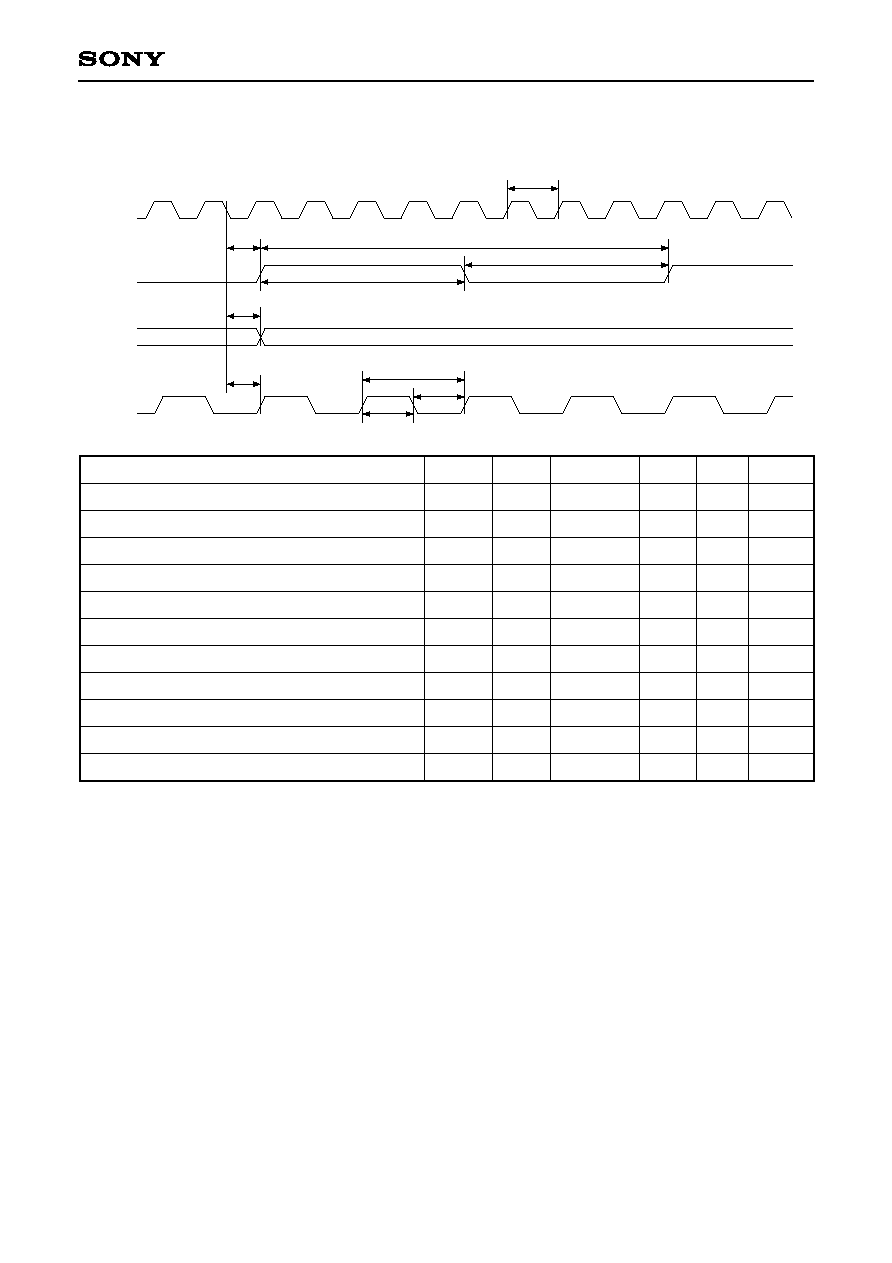
3-8. Video Sync Signal Input AC Characteristics
DCLK
t
HHSY
t
SHSY
HSYNC
t
HVSY
t
SVSY
VSYNC
t
HCBL
t
SCBL
CBLNK
t
HFID
t
SFID
FID
t
HHSY
t
SHSY
t
HVSY
t
SVSY
t
HCBL
t
SCBL
t
HFID
t
SFID
Item
HSYNC hold time
HSYNC setup time
VSYNC hold time
VSYNC setup time
CBLNK hold time
CBLNK setup time
FID hold time
FID setup time
t
HHSY
t
SHSY
t
HVSY
t
SVSY
t
HCBL
t
SCBL
t
HFID
t
SFID
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Symbol
Min.
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
When both inputting and outputting DCLK. For output, a load of 75pF is connected to DCLK.
≠ 14 ≠
CXD1852Q
3-9. fsc System Signal Output, DCLK Output AC Characteristics
XTL0O
t
CFSC
FSC
FHREF
DCLK
t
DFSC
t
DFHR
t
DDCK
t
WLFSC
t
WHFSC
t
CDCK
t
WHDCK
t
WLDCK
t
CX0
Item
FSC frequency
FSC cycle
FSC high level interval
FSC low level interval
FSC output delay time
FHREF output delay time
DCLK frequency
DCLK cycle
DCLK high level interval
DCLK low level interval
DCLK output delay time
f
FSC
t
CFSC
t
WHFSC
t
WLFSC
t
DFSC
t
DFHR
f
DCK
t
CDCK
t
WHDCK
t
WLDCK
t
DDCK
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
ns
ns
ns
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
Symbol
Min.
1/(i
◊
t
CX0
)
i
◊
t
CX0
i
◊
t
CX0
/2
i
◊
t
CX0
/2
--
--
1/(j
◊
t
CX0
)
j
◊
t
CX0
j
◊
t
CX0
/2
j
◊
t
CX0
/2
--
Typ.
--
--
--
--
15
15
--
--
--
--
15
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
The frequency division ratio i can be selected from 8 or 16.
2
The frequency division ratio j can be selected from 2 or 4.

≠ 15 ≠
CXD1852Q
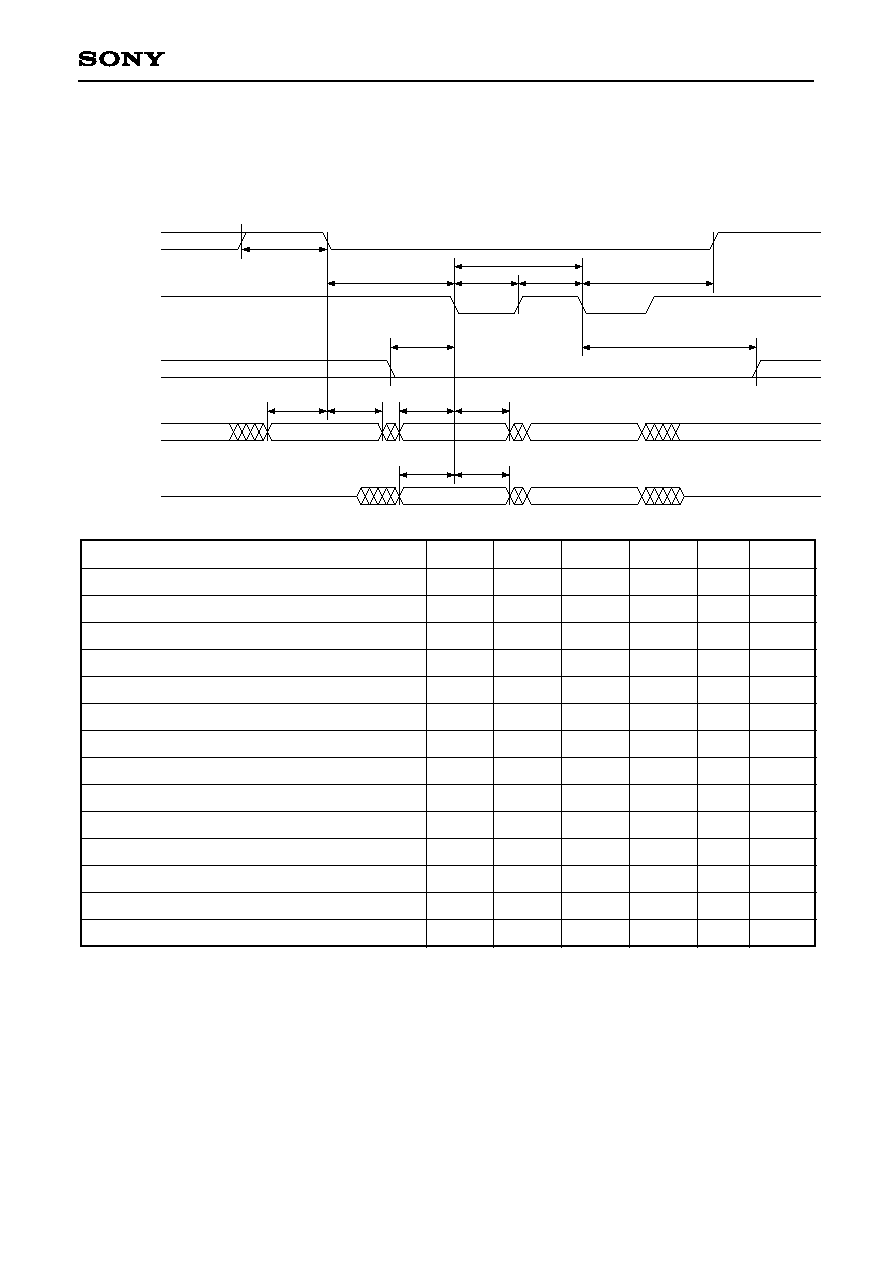
3-10. Audio Interface
t
DLRC
BCKO
DATO
LRCO
t
DDAT
t
BCKO
t
BCKO
Item
BCKO frequency
BCKO pulse width
DATO delay time (for BCKO)
LRCO delay time (for BCKO)
f
BCKO
t
BCKO
t
DDAT
t
DLRC
160
--
--
MHz
ns
ns
ns
Symbol
Min.
3.1
--
40
40
Max.
Unit
Remarks
≠ 16 ≠
CXD1852Q
3-11. DRAM Interface AC Characteristics
3-11-1. Write Cycle
t
RP
t
ASR
t
RAH
t
ASC
t
CAH
t
DS
t
DH
t
WCS
t
RCD
t
PC
t
CAS
t
CP
t
RSH
t
WCH
XRAS
XCAS0 to 3
XMWE
MA0 to 9
MD0 to 15
Item
RAS precharge time
RAS to CAS delay time
RAS hold time
Fast page mode cycle time
CAS pulse width
CAS precharge time
Write command setup time
Write command hold time
Row address setup time
Row address hold time
Column address setup time
Column address hold time
Write data setup time
Write data hold time
t
RP
t
RCD
t
RSH
t
PC
t
CAS
t
CP
t
WCS
t
WCH
t
ASR
t
RAH
t
ASC
t
CAH
t
DS
t
DH
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Symbol
Min.
2
◊
t
v
2
◊
t
v
t
v
2
◊
t
v
t
v
t
v
t
v
2
◊
t
v
t
v
t
v
t
v
t
v
t
v
t
v
Typ.
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
t
v is the basic clock cycle for the DRAM interface circuit.
2
Same as the DRAM interface read cycle.
≠ 17 ≠
CXD1852Q
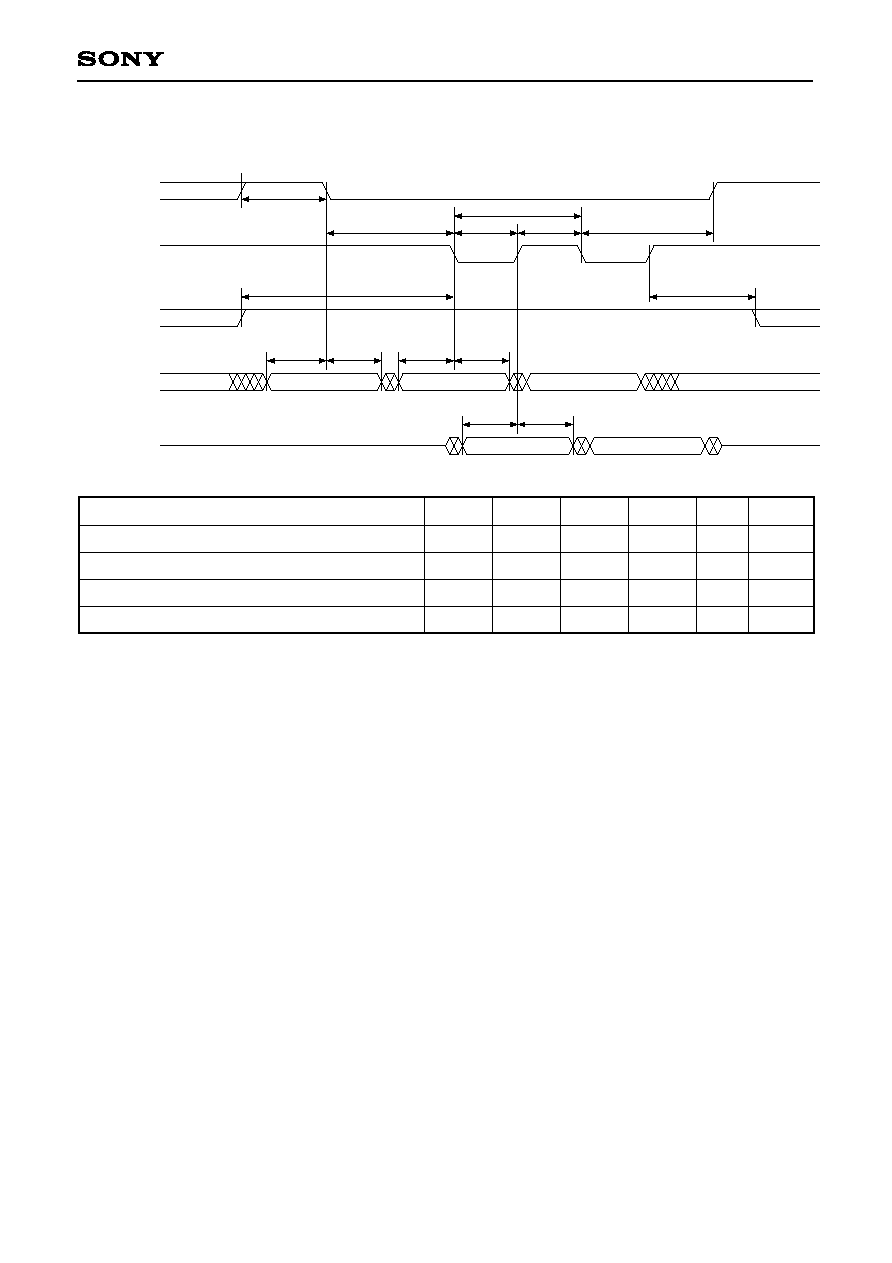
3-11-2. Read Cycle
t
RP
t
ASR
t
RAH
t
ASC
t
CAH
t
MDS
t
MDH
t
RCS
t
RCD
t
PC
t
CAS
t
CP
t
RSH
t
RCH
XRAS
XCAS0 to 3
XMWE
MA0 to 9
MD0 to 15
Item
Read command setup time
Read command hold time
Read data setup time
Read data hold time
t
RCS
t
RCH
t
MDS
t
MDH
ns
ns
ns
ns
Symbol
Min.
4
◊
t
v
t
v
2
8
Typ.
--
--
--
--
Max.
Unit
Remarks
1
t
v is the basic clock cycle for the DRAM interface circuit.
2
See the DRAM interface write cycle for items which appear in the timing chart but not in the table.
≠ 18 ≠
CXD1852Q
4. Description of Functions
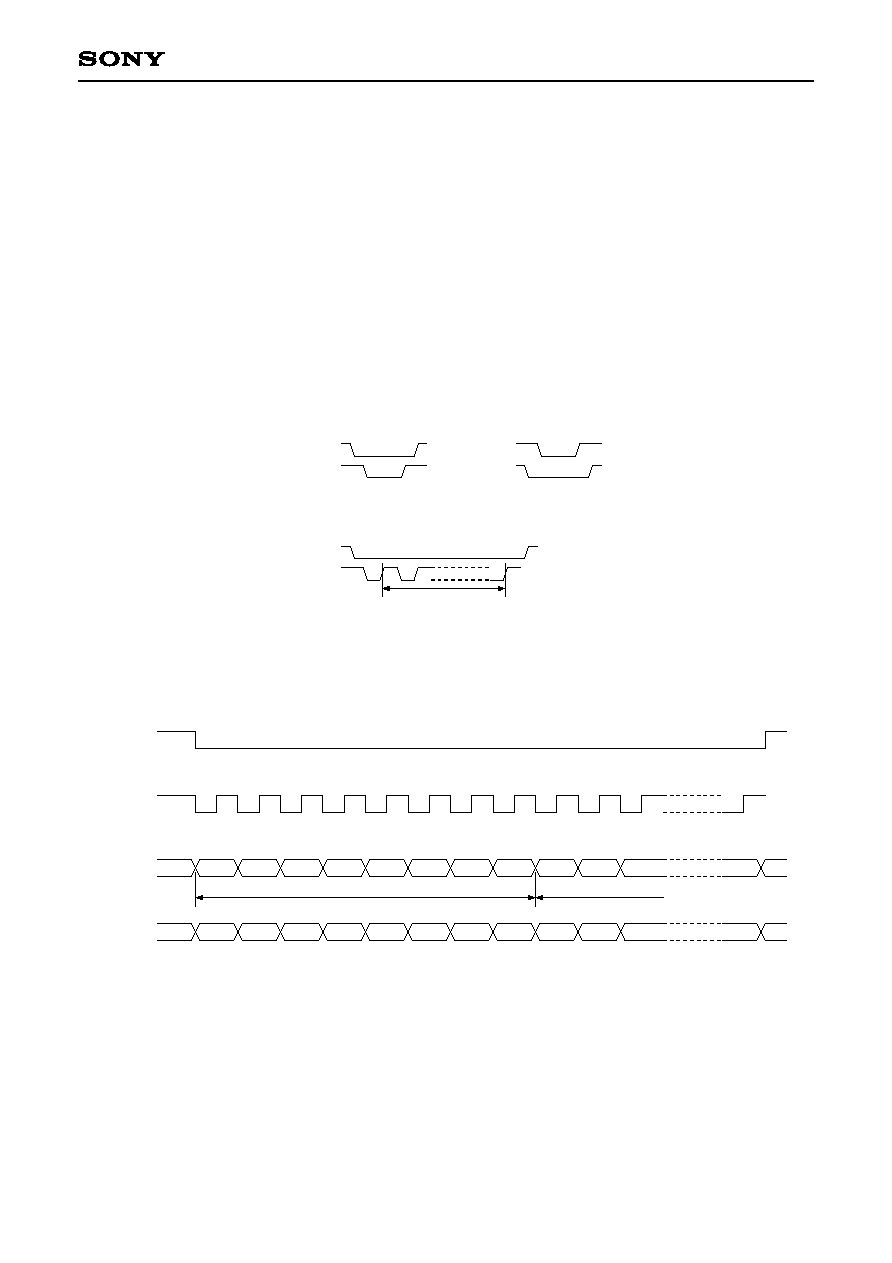
4-1. Host Interface Function
∑ The CXD1852Q operation is controlled by writing and reading registers. Write and read can also be
performed to an external DRAM via the registers. See the separately issued Register Manual for the
relationship between the registers and operation.
∑ The host interface operates while XHCS is low and does not operate while XHCS is high.
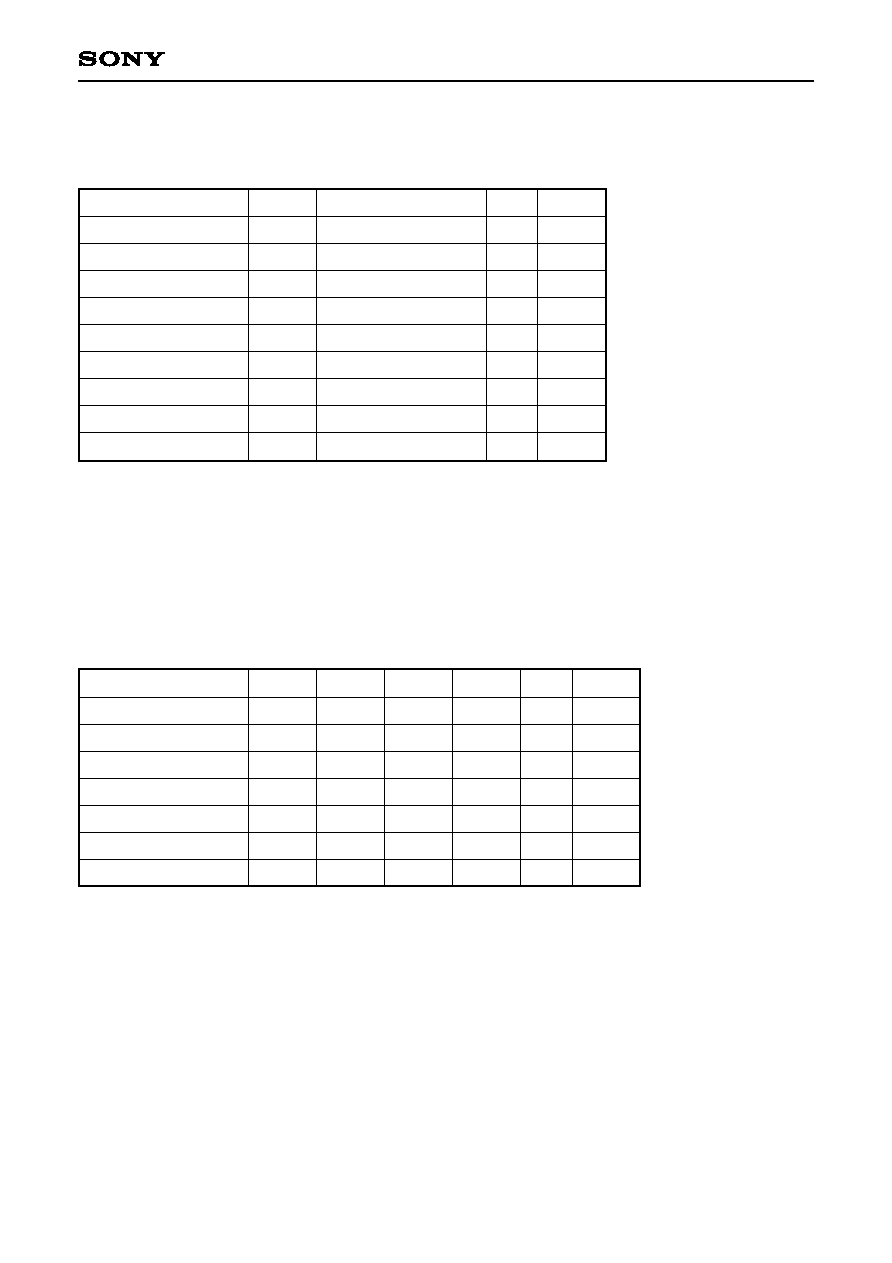
∑ The host interface operating mode can be set to 4-line serial or 8-bit parallel. The operating mode is selected
automatically at the end of the initial access after the hardware has been reset. (See the figure below.)
Registers are not accessed correctly until this selection has been determined, or in other words until the end
of the initial access after the hardware has been reset. Also, the HA3 to HA0 inputs should all be fixed low
during the operating mode selection access.
XHCS
HRW
XHCS
HRW
Access judged as parallel mode
XHCS
HRW
Access judged as serial mode
8 rises
∑ The serial mode signal format is as follows.
XHCS
HRW
(SCK)
bit0
bit1
bit2
bit3
bit4
bit5
bit6
bit7
bit8
bit9
byte0
byte1
HA0
(SI)
bit0
bit1
bit2
bit3
bit4
bit5
bit6
bit7
bit8
bit9
HD0
(SO)
1) In serial mode, input data is fetched in sync with the rise of HRW (SCK). Output data is synchronized with
the fall of HRW.
2) The initial byte (byte0) of the input after XHCS changes to low is a command. This command determines
the subsequent byte processing. See the following page for a description of commands and processing.
3) Input data is processed in one byte units. Therefore, when the final data consists of a number of bits which
is less than one byte, this deficient data is not processed. Be sure to input data with a number of bits which
is an integer multiple of 8. Also, the 0x20, 0x60, 0xA0 and 0xE0 commands process data in two byte units,
so data which is an even multiple of 8 should be input when using these commands.

≠ 19 ≠
CXD1852Q
Command
bit7 ∑∑∑ bit0
00000000
00010000
00100000
00110000
01100000
01110000
10000000
10010000
10100000
10110000
11100000
11110000
write
read
write
read
write
read
write
read
write
read
write
read
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
Register No.
Register No.
Register No.
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
Register No.
Register No.
Register No.
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register No.
+U/L byte select
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
LSB
first
LSB
first
LSB
first
LSB
first
LSB
first
LSB
first
MSB
first
MSB
first
MSB
first
MSB
first
MSB
first
MSB
first
No
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
Register data
don't care
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
Register data
don't care
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
Register data
don't care
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
Register data
(Lower byte)
don't care
Register data
don't care
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
Register data
(Upper byte)
don't care
write
read
2nd input byte 3rd input byte
4th input byte
Successive
odd-numbered
input bytes
Successive
even-numbered
input bytes
first
bit
Auto
inc.
Description of Commands
1) The "write read" column indicates whether that command writes data to or reads data from the registers.
2) Bytes marked with "Register No. + U/L byte select" specify the register to be accessed as well as whether
to access the upper or lower bytes of the register. The upper 7 bits specify the register No., and the
lowermost bit specifies the upper or lower bytes. When the lowermost bit is "0", the lower bytes are
selected, when "1", the upper bytes are selected.
3) Bytes marked with "Register No." specify the register to be accessed. The upper 7 bits specify the register
No., and the lowermost bit can be either "0" or "1".
4) The "Auto inc." column indicates the presence of the register No. auto increment function. For commands
without this function, the most recently input register No. is valid. For example, in case of the command
0x00, the register data input by the odd bytes is written to the register specified by the previous byte's input.
For the command 0x20, all subsequent data is written sequentially to the register specified by the 2nd input
byte.
5) For commands with the register No. auto increment function, the register specified by the 2nd input byte is
accessed first, and then access shifts to the register No. incremented by one each time the data for one
register (2 bytes) is read or written. For example, when using the command 0x60, if 0x08 is specified by the
2nd input byte, the 3rd and 4th input bytes are written to register 0x08, and the 5th and 6th input bytes are
written to register 0x09.
6) Bytes marked with "register data" are the data to be written to the registers during write commands.

≠ 20 ≠
CXD1852Q
7) When executing read commands, register data output starts from the 3rd output byte (bit 16). All earlier
output data is invalid data. Access shifts to a new register each time the output for one register (2 bytes) is
finished. For example, in case of the command 0x10, the byte data specified by the 2nd input byte is output
to the 3rd output byte, the other byte data in the same register is output to the 4th byte, and the byte data
specified by the 4th input byte is output to the 5th output byte.
8) The "first bit" column indicates whether LSB first or MSB first processing is performed for input or output of
the 2nd and subsequent bytes. This specification does not apply to the 1st byte (command). Commands
are normally LSB first. If LSB first is specified, processing is performed in the order where the initial bit in
each byte is LSB and the final bit is MSB. This order is reversed for MSB first. Note that for registers, bit 15
noted in the Register Manual is MSB and bit 0 is LSB.
4-2. DRAM Interface Function
∑ The applicable DRAMs are speed version 70 devices (RAS access time (Trac) of 70ns or less) with the fast
page mode function.
∑ When the total capacity of the external DRAM is 4 Mbits, use a 2CAS type DRAM with a configuration of 256
Kwords
◊
16 bits. When the total capacity is 8 Mbits, use two 2CAS type DRAMs with a configuration of 256
Kwords
◊
16 bits or 512 Kwords
◊
8 bits.
∑ Refresh is performed automatically using RAS-only-refresh. External control is not necessary.
∑ The DRAM is divided into the image frame memory, audio bit stream buffer, video bit stream buffer, user
data and on-memory register areas.
∑ The user data area can be used freely by the user, and CD-ROM decoded output can also be transferred to
this area. This area can be used to store video CD PSD, etc.
∑ The desired DRAM areas can be accessed from the control microcomputer via the registers.
4-3. CD-ROM Decoder Function
∑ CD signal processor LSI interface
The CD-ROM decoder has a CD signal processor LSI (CD-DSP) interface which directly interfaces the serial
data output from the CD-DSP. This interface supports a wide variety of input formats to enable connection
with general CD-DSP.
∑ CD-ROM data decoding (supports CD-ROM XA format mode2, form1 and form2)
CD-ROM data input from the CD-DSP supports CD-ROM XA format (mode2, form1 and form2).
∑ Input CD-ROM data is decoded by the CD-ROM decoder block. Also, the CD-DA signal input from the CD-
DSP can be output directly from the audio interface.
∑ The CD-ROM decoder has the following decoding and data transfer operating modes. The real-time
correction and write-only modes facilitate the loading of video CD PSD to the external DRAM, etc.
1) Auto transfer mode
The MPEG pack data within one sector of the video CD is automatically transferred to the system
decoder, where the audio stream sector or video stream sector can be decoded. This mode transfers
2324 bytes counted from the initial byte of user data within one sector to the system decoder.
2) Real-time correction mode
This mode executes error detection and correction processing for mode2, form1 sectors. The 2048 bytes
of user data within the error processed sector are transferred to the user area of the external DRAM. The
4 bytes of header information within the sector can also be loaded in the on-memory register within the
DRAM.
3) Write-only mode
This mode transfers the 2340 bytes of header, subheader and user data within one sector to the user area
of the external DRAM. When a form1 sector is input, error detection and correction processing is
performed and then the data is transferred to the buffer memory. When a form2 sector is input, the data is
transferred as is.

≠ 21 ≠
CXD1852Q
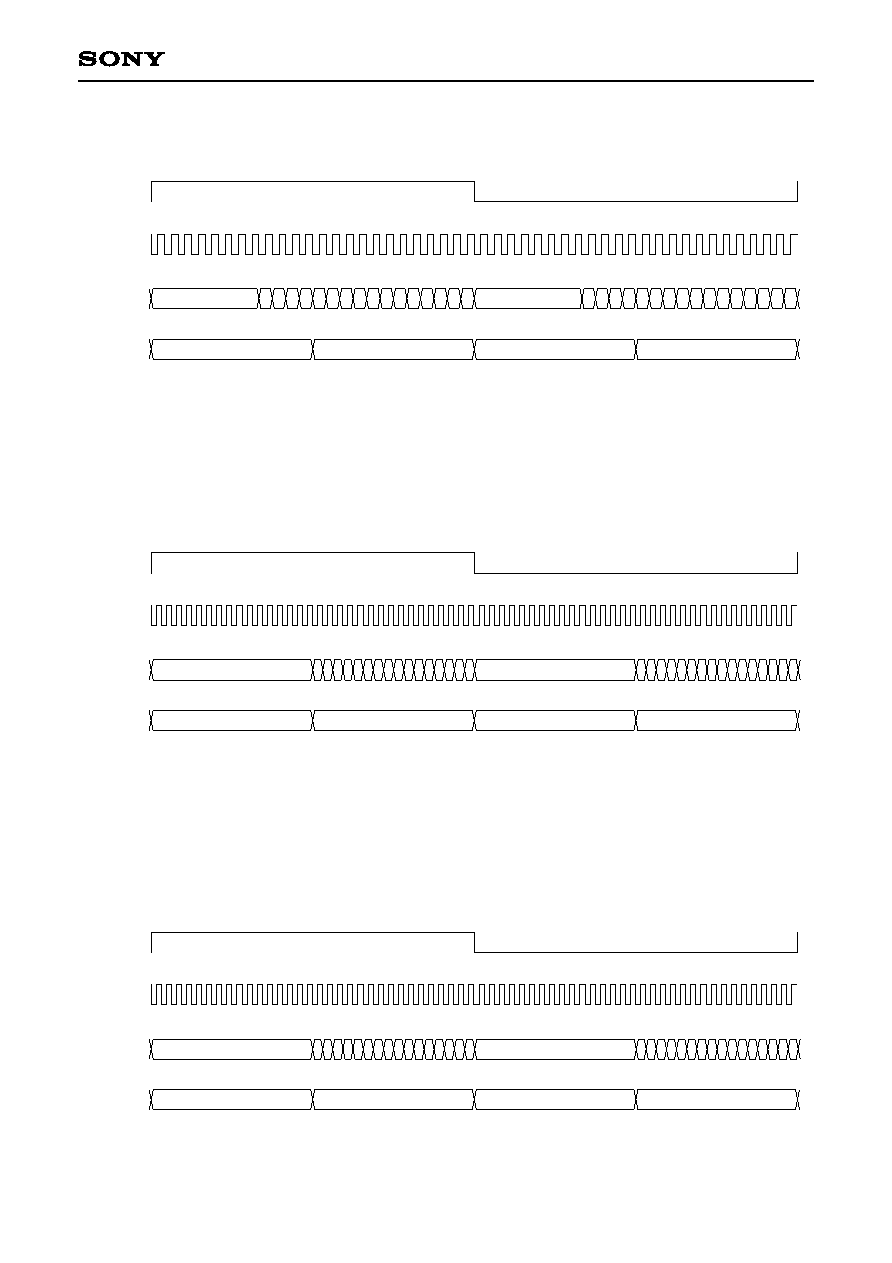
CD-DSP Input Signal Formats
1) 32-bit slot, MSB first, BCKMOD1, 0 = 00, LSBFST = 0
LRCI
BCKI
DATI
C2PO
Upper
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Lch
Rch
31
15 16
0
MSB
LSB MSB
LSB
Lower
Upper
Lower
2) 32-bit slot, LSB first, BCKMOD1, 0 = 00, LSBFST = 1
LRCI
BCKI
DATI
C2PO
Upper
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15
Lch
Rch
31
15 16
0
LSB
MSB LSB
MSB
Lower
Upper
Lower
3) 48-bit slot, MSB first, BCKMOD1, 0 = 01, LSBFST = 0
LRCI
BCKI
DATI
C2PO
Upper
Lch
Rch
47
23 24
0
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
Lower
Upper
Lower
D15 D14D13D12 D11D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D15 D14D13 D12D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
≠ 22 ≠
CXD1852Q
4) 48-bit slot, LSB first, BCKMOD1, 0 = 01, LSBFST = 1
LRCI
BCKI
DATI
C2PO
Upper
Lch
Rch
47
23 24
0
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
Lower
Upper
Lower
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11D12 D13D14 D15
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14D15
5) 64-bit slot, MSB first, BCKMOD1, 0 = 10, LSBFST = 0
LRCI
BCKI
DATI
C2PO
Upper
Lch
Rch
63
31 32
0
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
Lower
Upper
Lower
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
don't care
don't care
6) 64-bit slot, LSB first, BCKMOD1, 0 = 10, LSBFST = 1
LRCI
BCKI
DATI
C2PO
Upper
Lch
Rch
63
31 32
0
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
Lower
Upper
Lower
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
don't care
don't care

≠ 23 ≠
CXD1852Q
4-4. System Decoder Function
∑ The MPEG1 system layer (ISO/IEC 11172-1) is decoded, the audio and video bit streams are separated, and
each bit stream is transferred to the respective bit stream buffer.
∑ The MPEG1 bit stream input can be selected from either the built-in CD-ROM decoder or the host interface.
∑ The system decoder has a 128-word (256-byte) FIFO for the bit stream input.
∑ Audio and video sync playback are controlled according to the time stamp within the bit stream.
4-5. Video Decoder Function
∑ The MPEG1 video layer (ISO/IEC 11172-2) is decoded. This function supports the range where
constrained_parameter_flag = "1" and video CD high resolution still picture.
∑ Video CD high resolution still picture (NTSC, PAL) can be decoded with a single external 4-Mbit DRAM.
∑ Special decoding functions are as follows. Slow playback, fast forward and other modes can be realized by
combining these functions.
I-Play: Only I-Pictures are decoded.
Still (Pause): Decoding is paused.
1 Frame Play: Only one frame (picture) is decoded.
IP-Play: Only I and P-Pictures are decoded.
IPB-Play: Alternate frames of continuous B-Pictures and all I and P-Pictures are decoded.
∑ This function supports digest play.
∑ The various information in the bit stream is loaded to the on-memory register area within the external DRAM.
4-6. Video Post Processor and Sync Generator Functions
∑ The image data output format can be selected from 24-bit RGB, 24-bit YCbCr and 16-bit YCbCr. See the
following page.
∑ Fade in and fade out are allowed.
∑ Image enlargement and reduction are allowed.
∑ The CXD1852Q contains an OSD color table and selector, and OSD display is achieved by inputting the
OSD character signal.
∑ The video sync signal can be generated using the built-in sync generator. Image data can also be output in
sync with an externally input video sync signal.
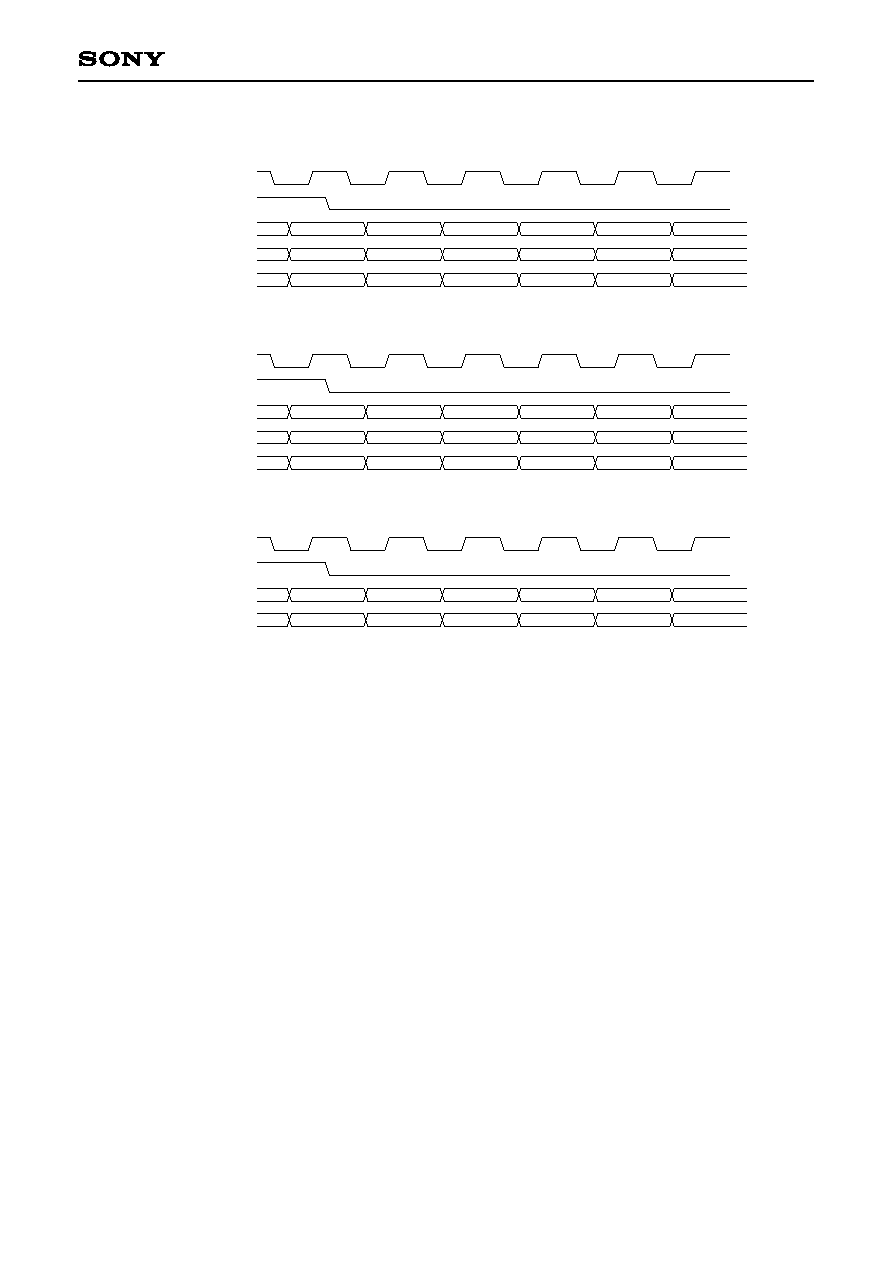
≠ 24 ≠
CXD1852Q
DCLK
R (n)
HSYNC
R0 to 7
R (n + 1)
R (0)
R (1)
R (2)
R (3)
G (n)
G0 to 7
G (n + 1)
G (0)
G (1)
G (2)
G (3)
B (n)
B0 to 7
B (n + 1)
B (0)
B (1)
B (2)
B (3)
24-bit RGB output format
DCLK
Y (n)
HSYNC
Y0 to 7
Y (n + 1)
Y (0)
Y (1)
Y (2)
Y (3)
Cb (n)
Cb0 to 7
Cb (n + 1)
Cb (0)
Cb (1)
Cb (2)
Cb (3)
Cr (n)
Cr0 to 7
Cr (n + 1)
Cr (0)
Cr (1)
Cr (2)
Cr (3)
24-bit YCbCr output format
DCLK
Y (n)
HSYNC
Y0 to 7
Y (n + 1)
Y (0)
Y (1)
Y (2)
Y (3)
Cb (n)
C0 to 7
Cr (n)
Cb (0)
Cr (0)
Cb (2)
Cr (2)
16-bit YCbCr output format
Note)
∑ The subscript (i) indicates the data for pixel i.
∑ The above timing charts show the timing when the pixel data output is synchronized with the fall of DCLK.
The pixel data output can also be synchronized with the rise of DCLK.

≠ 25 ≠
CXD1852Q
4-7. Audio Decoder Function
∑ MPEG audio stream decoding is performed for MPEG1 standard (ISO/IEC 11172-3) layer 1 and layer 2.
∑ Monaural, dual, stereo and joint stereo decoding modes are supported.
∑ All MPEG1 standard sampling frequencies (32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz) are supported.
∑ All MPEG1 standard bit rates are supported.
Layer 1: 32Kbps (monaural/stereo) to 448Kbps (monaural/stereo)
Layer 2: 32Kbps (monaural) to 384Kbps (stereo)
∑ The audio decoder's audio interface output port is equipped with a PCM audio output which outputs decoded
audio data in bit serial format and a digital audio interface output (digital out). The audio interface is set by
setting the internal registers.
1) LRCK and BCK generation
The LR clock and bit clock can be generated by frequency dividing the clock input from external pins XTLI
or FSXI. The generated clocks are output from the BCKO and LRCO pins, respectively. LRCO and BCKO
can be output in the desired polarity. Also, the number of slots per sample supports the three types of 32,
48 and 64 bit clocks/LRCK.
2) PCM audio output format
The PCM audio output format can be set to any of the following combinations to allow connection with a
wide range of 1-bit D/A converters.
16-bit word length, MSB first or LSB first, frontward truncation or rearward truncation
18-bit word length, MSB first or LSB first, frontward truncation or rearward truncation
20-bit word length, MSB first or LSB first, frontward truncation or rearward truncation
24-bit word length, MSB first or LSB first, frontward truncation or rearward truncation
3) Digital out format
The digital out output format supports the type2, form1 format for consumer use. The output word length
can be selected from 16, 18, 20 or 24 bits.
4) Decoded channel assignment
Channels 1 and 0 of the audio sample obtained by decoding the MPEG audio stream can be assigned to
the L and R channel outputs in any combination.
5) Audio mute
The audio output contains a zero-cross mute circuit. Zero-cross detection is performed for 44 sample
sections (approximately 0.1ms when fs = 44.1kHz), and if zero-cross is not detected, the output is forcibly
muted.
6) Attenuator
The audio output contains an attenuator circuit. Attenuation of ≠12dB can be obtained by setting the
internal register.
7) CD-DA output mode
When playing back a CD-DA disc, the data input from the CD-DSP can be output directly from the PCM
audio output (DATO) and the digital audio interface output port (DOUT). Output ports LRCO and BCKO can
also select and output the clock inputs LRCI and BCKI from the CD-DSP.

≠ 26 ≠
CXD1852Q
PCM Audio Output Formats
1) 64-bit slot, frontward truncation, LSB first, OSLT1, 0 = 10, OTRUNK = 1, OLSBFST = 1
LRCO
BCKO
DATO
Lch
Rch
63
31 32
0
LSB
MSB
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
LSB
MSB
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
DAL1, 0 = 11
DAL1, 0 = 10
DAL1, 0 = 01
DAL1, 0 = 00
2) 64-bit slot, rearward truncation, LSB first, OSLT1, 0 = 10, OTRUNK = 0, OLSBFST = 1
LRCO
BCKO
DATO
Lch
Rch
63
31 32
0
LSB
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
LSB
MSB
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
DAL1, 0 = 11
DAL1, 0 = 10
DAL1, 0 = 01
DAL1, 0 = 00
MSB
LSB/MSB first setting
OLSBF = 1: set to LSB first
OLSBF = 0: set to MSB first
Data word length setting
DAL1, 0 = 11: 24 bits
DAL1, 0 = 10: 20 bits
DAL1, 0 = 01: 18 bits
DAL1, 0 = 00: 16 bits

≠ 27 ≠
CXD1852Q
3) 48-bit slot, frontward truncation, LSB first, OSLT1, 0 = 01, OTRUNK = 1, OLSBFST = 1
LRCO
BCKO
DATO
Lch
Rch
47
23 24
0
LSB
MSB
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17 D18D19 D20D21 D22D23
LSB
MSB
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17 D18 D19D20 D21D22 D23
DAL1, 0 = 11
DAL1, 0 = 10
DAL1, 0 = 01
DAL1, 0 = 00
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17 D18D19
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17 D18 D19
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12D13 D14D15
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14D15
4) 48-bit slot, rearward truncation, LSB first, OSLT1, 0 = 01, OTRUNK = 0, OLSBFST = 1
LRCO
BCKO
DATO
Lch
Rch
47
23 24
0
LSB
MSB
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17 D18D19 D20D21 D22
LSB
MSB
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17 D18 D19D20 D21D22 D23
DAL1, 0 = 11
DAL1, 0 = 10
DAL1, 0 = 01
DAL1, 0 = 00
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14D15 D16D17 D18
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12 D13D14 D15D16 D17D18 D19
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14 D15D16
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11D12 D13D14 D15D16 D17
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10D11 D12D13 D14
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11D12 D13D14 D15
D23 D0
D19
D17
D15
LSB/MSB first setting
OLSBF = 1: set to LSB first
OLSBF = 0: set to MSB first
Data word length setting
DAL1, 0 = 11: 24 bits
DAL1, 0 = 10: 20 bits
DAL1, 0 = 01: 18 bits
DAL1, 0 = 00: 16 bits
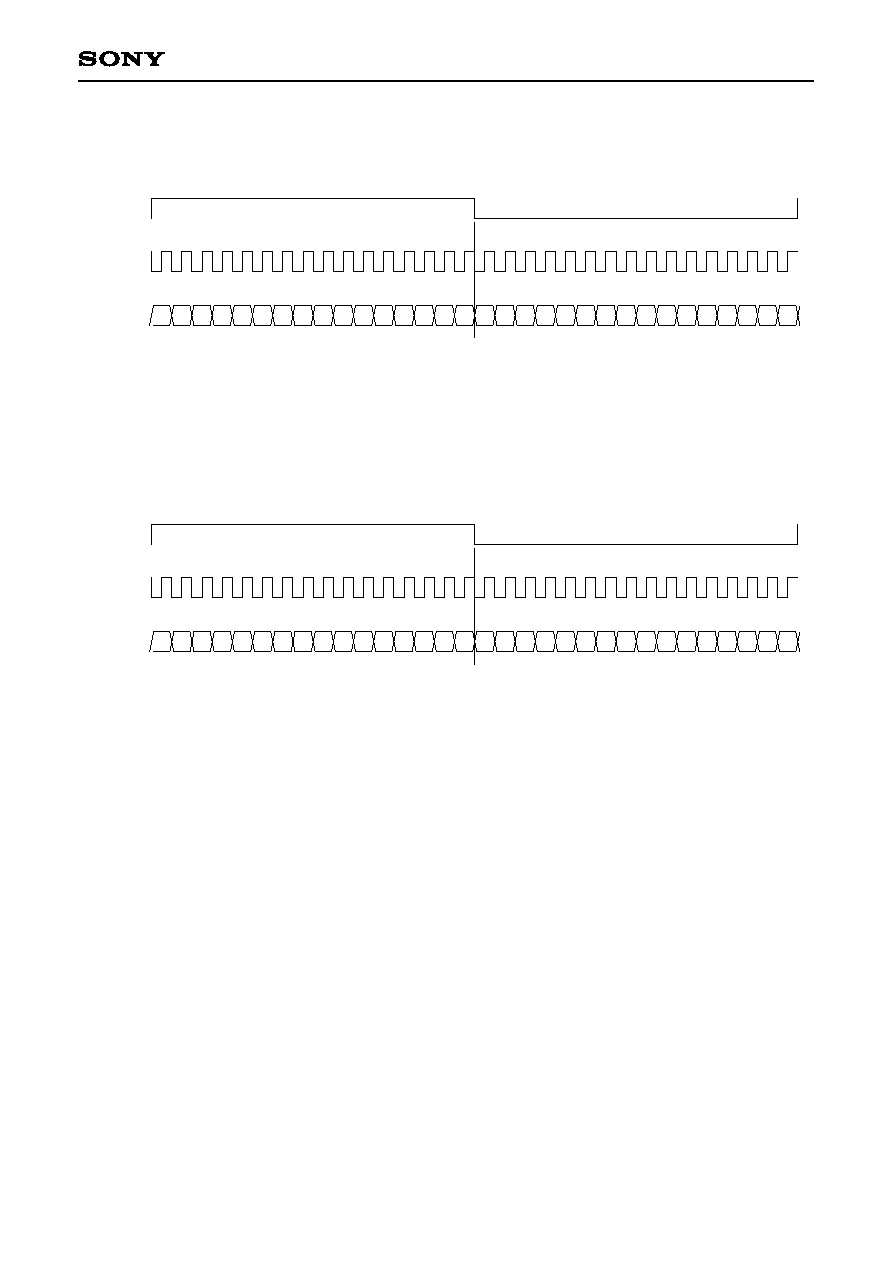
≠ 28 ≠
CXD1852Q
5) 32-bit slot, LSB first, OSLT1, 0 = 00, OLSBFST = 1
LRCO
BCKO
DATO
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15 D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15
Lch
Rch
31
15 16
0
LSB
MSB LSB
MSB
6) 32-bit slot, MSB first, OSLT1, 0 = 00, OLSBFST = 0
LRCO
BCKO
DATO
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Lch
Rch
31
15 16
0
MSB
LSB MSB
LSB
LSB/MSB first setting
OLSBF = 1: set to LSB first
OLSBF = 0: set to MSB first
Data word length: 16 bits

≠ 29 ≠
CXD1852Q
Digital Audio Interface Output Formats
1) 24 bits/word
Sync
preamble
LSB
0
3
4
MSB
27
V
U
C
P
28 29 30 31
Validity flag
User data
Channel status
Parity
2) 20 bits/word
Sync
preamble
0
3
4
MSB
27
V
U
C
P
28 29 30 31
(0) data
LSB
7
8
3) 18 bits/word
Sync
preamble
0
3
4
MSB
27
V
U
C
P
28 29 30 31
(0) data
LSB
9
10
4) 16 bits/word
Sync
preamble
0
3
4
MSB
27
V
U
C
P
28 29 30 31
(0) data
LSB
11
12
Data word length setting
DOL1, 0 = 11: 24 bits
DOL1, 0 = 10: 20 bits
DOL1, 0 = 01: 18 bits
DOL1, 0 = 00: 16 bits

≠ 30 ≠
CXD1852Q
Package Outline
Unit: mm
SONY CODE
EIAJ CODE
JEDEC CODE
M
PACKAGE STRUCTURE
PACKAGE MATERIAL
LEAD TREATMENT
LEAD MATERIAL
PACKAGE WEIGHT
EPOXY RESIN
SOLDER PLATING
COPPER / 42 ALLOY
31.2 Ī 0.2
28.0 Ī 0.2
0.35 Ī 0.1
0.8
30
1
61
90
60
31
91
120
0.15 Ī 0.1
0į to 10į
(29.6)
0.8 Ī
0.2
0.16
0.1
0.15 ≠ 0.05
+ 0.1
A
0.15 Ī 0.1
3.45 Ī 0.25
QFP-120P-L01
QFP120-P-2828-A
120PIN QFP (PLASTIC)
4.9g
DETAIL A





























