 | –≠–Ľ–Ķ–ļ—ā—Ä–ĺ–Ĺ–Ĺ—č–Ļ –ļ–ĺ–ľ–Ņ–ĺ–Ĺ–Ķ–Ĺ—ā: TMS416100 | –°–ļ–į—á–į—ā—Ć:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

TMS416100, TMS416100P
16777216-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORIES
SMKS611 ≠ FEBRUARY 1994
Copyright
©
1994, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
∑
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251≠1443
This data sheet is applicable to all
TMS416100/Ps symbolized with Revision "B"
and subsequent revisions as described on
page 24.
∑
Organization . . . 16 777 216
◊
1
∑
Single 5-V Power Supply (
Ī
10% Tolerance)
∑
Performance Ranges:
ACCESS ACCESS ACCESS
READ
TIME
TIME
TIME
OR WRITE
tRAC
tCAC
tAA
CYCLE
(MAX )
(MAX )
(MAX )
(MIN)
'416100- 60
60 ns
15 ns
30 ns
110 ns
'416100- 70
70 ns
18 ns
35 ns
130 ns
'416100- 80
80 ns
20 ns
40 ns
150 ns
∑
Enhanced Page Mode Operation for Faster
Memory Access
∑
CAS-Before-RAS Refresh
∑
Long Refresh Period
≠ 4096 Cycle Refresh in 64 ms
(TMS416100)
≠ 256 ms for Extended Refresh Version
(TMS416100P)
∑
3-State Unlatched Output
∑
Low Power Dissipation (TMS416100P Only)
≠ 500-
Ķ
A CMOS Standby Current
≠ 500-
Ķ
A Self-Refresh Current
≠ 500-
Ķ
A Extended Refresh Battery Backup
Current
∑
All Inputs, Outputs and Clocks Are TTL
Compatible
∑
Operating Free-Air Temperature Range:
0
į
C to 70
į
C
description
The TMS416100/P series are high-speed, 16 777 216-bit dynamic random-access memories, organized as
16 777 216 words of one bit each. The TMS416100P series feature self refresh and extended refresh. They
employ state-of-the-art EPIC
TM
(Enhanced Performance Implanted CMOS) technology for high performance,
reliability, and low power at a low cost.
These devices feature maximum RAS access times of 60 ns, 70 ns, and 80 ns. All inputs, outputs, and clocks
are compatible with Series 74 TTL. All addresses and data-in lines are latched on chip to simplify system design.
Data out is unlatched to allow greater system flexibility.
The TMS416100/P are offered in 300-mil 24/26-lead plastic surface-mount SOJ packages (DJ suffix) and
24/26-lead plastic small-outline packages (DGA suffix). All packages are characterized for operation from 0
į
C
to 70
į
C.
PIN NOMENCLATURE
A0 ≠ A11
Address Inputs
CAS
Column-Address Strobe
D
Data In
Q
Data Out
NC
No Internal Connection
RAS
Row-Address Strobe
VCC
5-V Supply
VSS
Ground
W
Write Enable
1
2
3
4
5
6
V
CC
D
NC
W
RAS
A11
8
9
10
11
12
13
A10
A0
A1
A2
A3
V
CC
19
18
17
16
15
14
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
V
SS
V
SS
Q
NC
CAS
NC
A9
26
25
24
23
22
21
DJ PACKAGE
( TOP VIEW )
V
CC
D
NC
W
RAS
A11
26
25
24
23
22
21
19
18
17
16
15
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
V
SS
Q
NC
CAS
NC
A9
8
9
10
11
12
13
A10
A0
A1
A2
A3
V
CC
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
V
SS
DGA PACKAGE
( TOP VIEW )
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
EPIC is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
TMS416100, TMS416100P
16777216-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORIES
SMKS611 ≠ FEBRUARY 1994
2
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
∑
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251≠1443
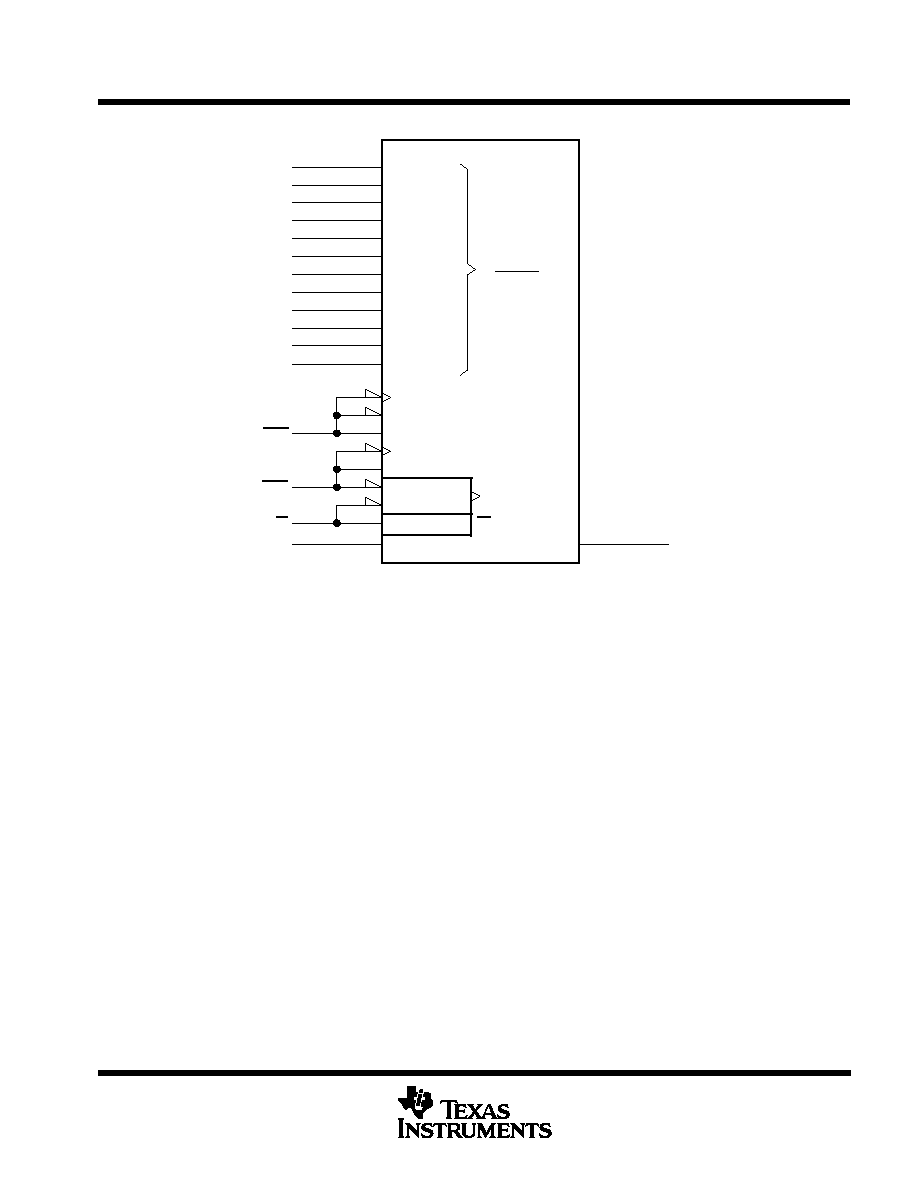
logic symbol
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
RAS
CAS
W
D
9
10
11
12
15
16
17
18
19
21
5
23
4
2
30D12/21D0
31D23/21D11
C30 [ROW]
G33 [REFRESH ROW]
34 [PWR DWN]
C31 [COL]
G34
33C32
33, 31D
34 EN
A, 32D
A
0
16 383K
RAM 16 384K
◊
1
&
A10
8
27
Q
A
A11
6
This symbol is in accordance with ANSI/IEEE Std 91-1984 and IEC Publication 617-12.
Pin numbers shown are for the DJ and DGA packages.
TMS416100, TMS416100P
16777216-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORIES
SMKS611 ≠ FEBRUARY 1994
3
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
∑
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251≠1443
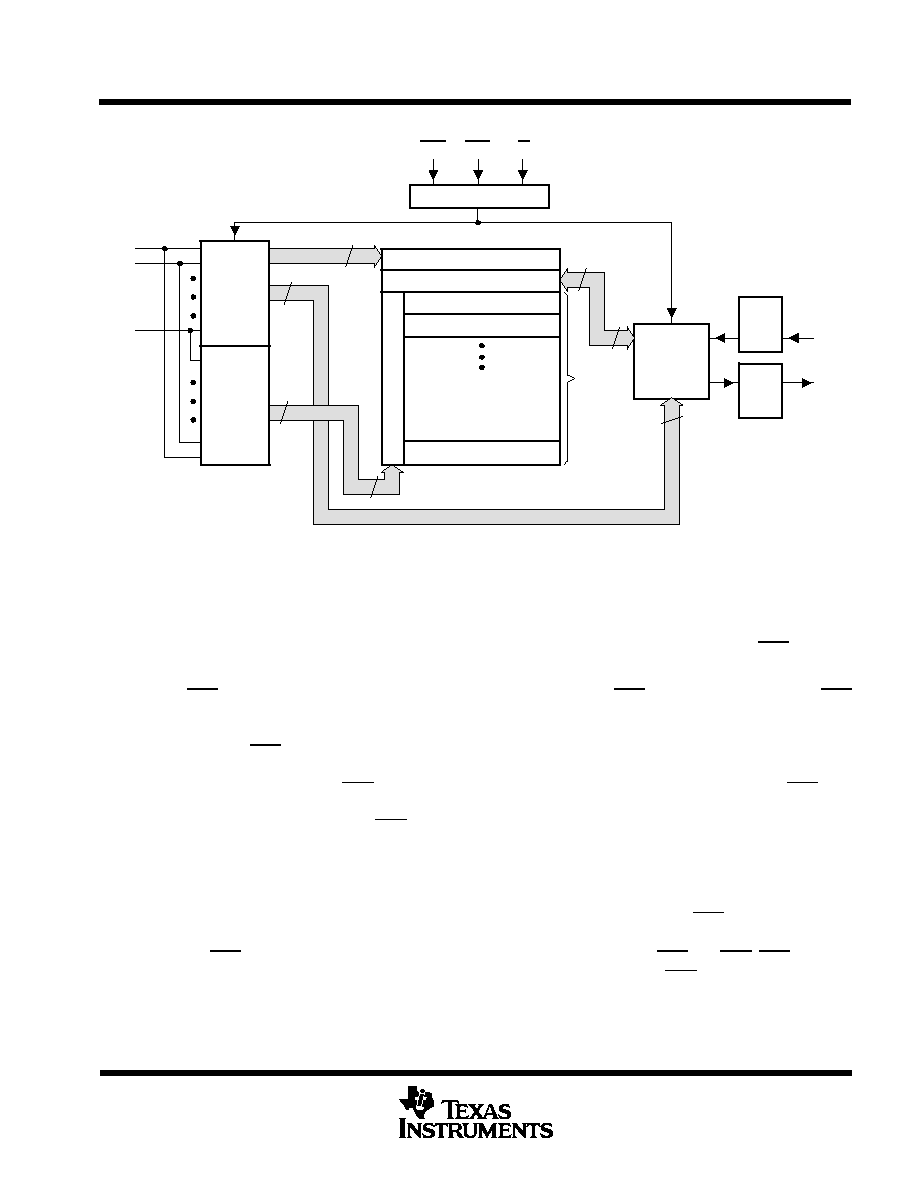
functional block diagram
A0
A1
A11
2
10
12
12
4
4
2
Timing and Control
Column-
Address
Buffers
Row-
Address
Buffers
I/O
Buffers
1 of 4
Selection
Data
In
Reg.
Data
Out
Reg.
Column Decode
Sense Amplifiers
64
256K Array
256K Array
256K Array
RAS
CAS
W
Row Decode
D
Q
operation
enhanced page mode
Enhanced page-mode operation allows faster memory access by keeping the same row address while selecting
random column addresses. The time for row-address setup and hold and address multiplex is thus eliminated.
The maximum number of columns that can be accessed is determined by t
RASP
, the maximum RAS-low time.
Unlike conventional page-mode DRAMs, the column-address buffers in this device are activated on the falling
edge of RAS. The buffers act as transparent or flow-through latches while CAS is high. The falling edge of CAS
latches the addresses and enables the output. This feature allows the TMS416100/P to operate at a higher data
bandwidth than conventional page-mode parts because retrieval begins as soon as the column address is valid
rather than when CAS transitions low. This performance improvement is referred to as
enhanced page mode.
Valid column address can be presented immediately after row-address hold time has been satisfied, usually well
in advance of the falling edge of CAS. In this case, data is obtained after t
CAC
max (access time from CAS low),
if t
AA
max (access time from column address) and t
RAC
have been satisfied. In the event that the column address
for the next cycle is valid at the time CAS goes high, access time for the next cycle is determined by the later
occurrence of t
CPA
or t
CAC
.
address (A0 ≠ A11)
Twenty-four address bits are required to decode 1 of 16 777 216 storage cell locations. Twelve row-address bits
are set up on inputs A0 through A11 and latched during a normal access and during RAS-only refresh as the
device requires 4096 refresh cycles. Twelve column-address bits are set up on inputs A0 ≠ A11 and latched onto
the chip by CAS. All addresses must be stable on or before the falling edges of RAS and CAS. RAS is similar
to a chip enable in that it activates the sense amplifiers as well as the row decoder. CAS is used as a chip select,
activating the output buffer as well as latching the address bits into the column-address buffer.
TMS416100, TMS416100P
16777216-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORIES
SMKS611 ≠ FEBRUARY 1994
4
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
∑
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251≠1443
write enable ( W )
The read or write mode is selected through the write-enable ( W ) input. A logic high on the W input selects the
read mode and a logic low selects the write mode. The write-enable terminal can be driven from standard TTL
circuits without a pullup resistor. The data input is disabled when the read mode is selected. When W goes low
prior to CAS (early write), data out remains in the high-impedance state for the entire cycle, permitting common
I/O operation.
data in (D)
Data is written during a write or read-modify-write cycle. Depending on the mode of operation, the falling edge
of CAS or W strobes data into the on-chip data latch. In an early-write cycle, W is brought low prior to CAS and
the data is strobed in by CAS with setup and hold times referenced to this signal. In a delayed-write or
read-modify-write cycle, CAS is already low and the data is strobed in by W with setup and hold times referenced
to this signal.
data out (Q)
The 3-state output buffer provides direct TTL compatibility (no pullup resistor required) with a fanout of two
Series 74 TTL loads. The output is in the high-impedance (floating) state until CAS is brought low. In a read cycle,
the output becomes valid at the latest occurrence of t
RAC
, t
AA
, t
CAC
, or t
CPA
and remains valid while CAS is low.
CAS going high returns it to the high-impedance state.
refresh
A refresh operation must be performed at least once every 64 ms to retain data. This can be achieved by strobing
each of the 4096 rows (A0 ≠ A11). A normal read or write cycle refreshes all bits in each row that is selected.
A RAS-only operation can be used by holding CAS at the high (inactive) level, conserving power as the output
buffer remains in the high-impedance state. Externally generated addresses must be used for a RAS-only
refresh. Hidden refresh can be performed by holding CAS at V
IL
after a read operation and cycling RAS after
a specified precharge period, similar to a RAS-only refresh cycle except with CAS held low. Valid data is
maintained at the output throughout the hidden refresh cycle. An internal address provides the refresh address
during hidden refresh.
CAS-before-RAS refresh
CAS-before-RAS (CBR) refresh is utilized by bringing CAS low earlier than RAS (see parameter t
CSR
) and
holding it low after RAS falls (see parameter t
CHR
). For successive CAS-before-RAS refresh cycles, CAS
remains low while cycling RAS. For this mode of refresh, the external addresses are ignored and the refresh
address is generated internally.
A low-power battery-backup refresh mode that requires less than 500
Ķ
A refresh current is available on the
TMS416100P. Data integrity is maintained using CAS-before-RAS refresh with a period of 62.5
Ķ
s while holding
RAS low for less than 1
Ķ
s. To minimize current consumption, all input levels need to be at CMOS levels
(V
IL
0.2 V, V
IH
V
CC
≠ 0.2 V).
power up
To achieve proper device operation, an initial pause of 200
Ķ
s followed by a minimum of eight initialization cycles
is required after full V
CC
level is achieved. These eight initialization cycles need to include at least one refresh
(RAS-only or CAS-before-RAS) cycle.

TMS416100, TMS416100P
16777216-BIT
DYNAMIC RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORIES
SMKS611 ≠ FEBRUARY 1994
5
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
∑
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251≠1443
self refresh ( TMS416100P)
The self-refresh mode is entered by dropping CAS low prior to RAS going low. CAS and RAS are both held low
for a minimum of 100
Ķ
s. The chip is then refreshed by an on-board oscillator. No external address is required
because the CBR counter is used to keep track of the address. To exit the self-refresh mode, both RAS and CAS
are brought high to satisfy t
CHS
. Upon exiting the self-refresh mode, a burst refresh (refresh a full set of row
addresses) must be executed before continuing with normal operation. This ensures the DRAM is fully
refreshed.
test mode
The test mode is initiated with a CAS-before-RAS refresh cycle while simultaneously holding the W input low
(WCBR). The entry cycle performs an internal refresh cycle while internally setting the device to perform parallel
read or write on subsequent cycles. While in the test mode, any data sequence can be performed. The device
exits the test mode if a CAS-before-RAS (CBR) refresh cycle with W held high or a RAS-only refresh (ROR) cycle
is performed.
The device is configured as 1024K
◊
16 bits with a 16-bit parallel read-and-write data path in the test mode.
Column addresses A0, A1, A10, and A11 are not used. During a read cycle, all 16 bits of the internal data bus
are compared. If all bits are in the same data state, the output pin goes high. If one or more bits disagree, the
output pin goes low. Test time is reduced by a factor of 16, compared to normal memory mode.
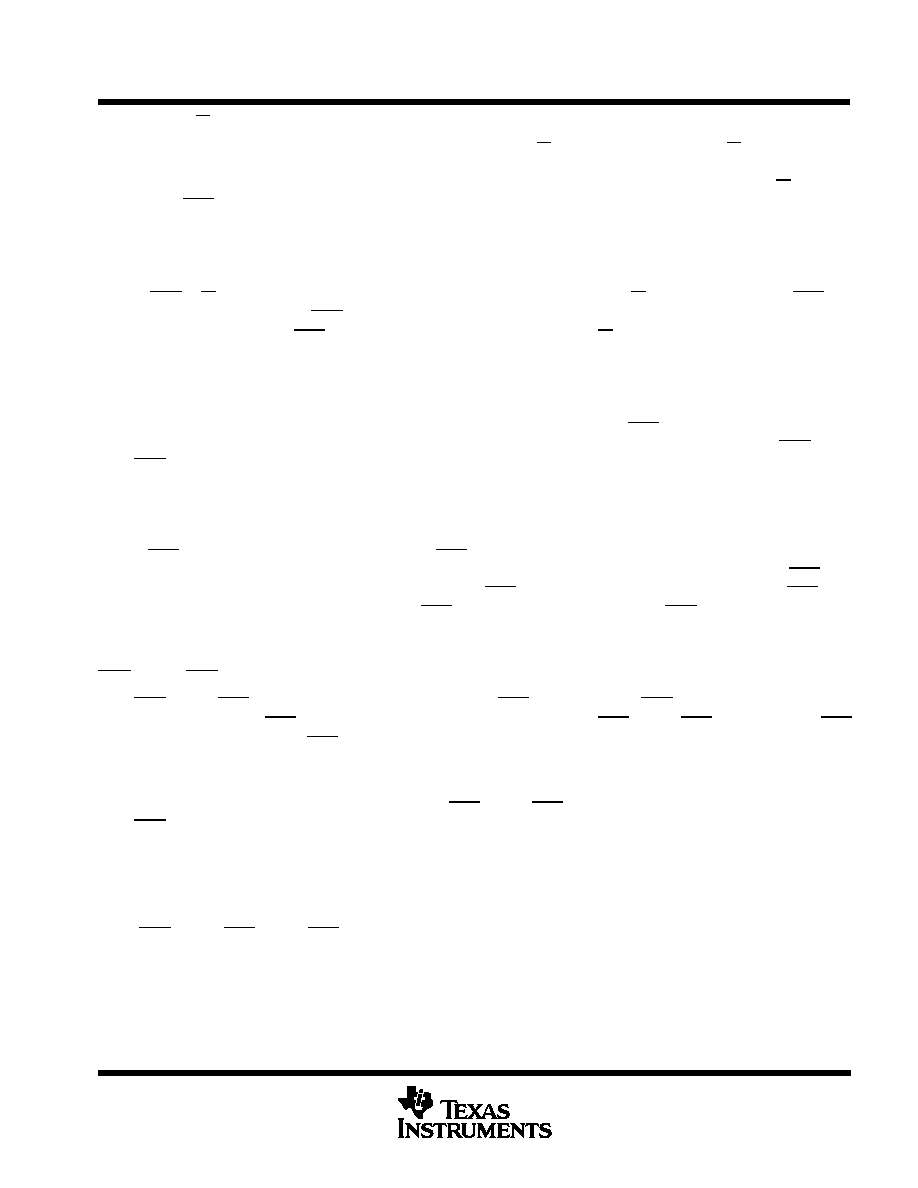
RAS
CAS
W
Test-Mode Cycle
Entry
Cycle
Exit
Cycle
Normal
Mode
NOTE: The states of W, data input, and address are defined by the type of cycle used during test mode.
Figure 1. Test-Mode Cycle




